How to Get Page Load Time in Angular?
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
In web development, performance is the most important thing. Users expect fast and responsive web applications and even minor delays can impact user experience and satisfaction. Monitoring page load time is important for identifying performance bottlenecks and optimizing the user experience. In this article, we'll explore how to get page load time in Angular 15.
Prerequisites
What is Page Load Time?
Page load time, also known as page load speed, refers to the time it takes for a web page to fully load in a user's browser. It includes the time taken to fetch and render all the necessary resources, such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and other assets. Measuring page load time provides valuable insights into the performance of web applications and helps identify areas for improvement.
Approach
- We will create a component, interceptor, module and routing module files.
- In the routing module, we will add our routing for all components. We will register the components, modules and interceptors in the module file.
- We will create app component and in the app component, we will capture the routing events with angular router NavigationStart and NavigationEnd. The app component is our base component and the routing for all the component will be shown through the app component.
- Therefore, any redirection to page the routing event will trigger and events will be captured in the app component. We will log the routing time, store it in the variable and render in the HTML. You can find the code later.
- We will create HTTP interceptor to capture API loading time. Therefore, whenever HTTP request hits, It will go through the interceptor and will capture the API loading time by start and end.
Steps to Get page Load Time
Step 1: Install Angular CLI
- First you need to install Node.js on your system.
- Second, open your terminal or CMD(Command prompt) and run the below command
npm install -g @angular/cli
Step 2: Create a new Angular application
Run the below command to create a new Angular application
ng new angular-api-routing-time
Step 3: Redirect to project directory
Change you working directory by entering project name in the below command
cd angular-api-routing-time
Step 4: Execute an application
ng serve --open
The --open flag open an application directly in a browser. The application default run on http://localhost:4200.
After completing project creation and setup, you need create Components, Service, Module and Interceptor and the structure will be display like the below image.
Step 5: Create component
ng generate component home ng g c about
The above command will create a component in the app directory. You can shorthand the command by writing ng g c.
Step 6: Create interceptors
ng generate interceptor application
The above command will create interceptor in the app directory.
Step 7: Create Module with Routing
ng generate module app --routing
The above command will generate module with routing. Here it will generate app.module.ts and app-routing.module.ts.
Folder Structure
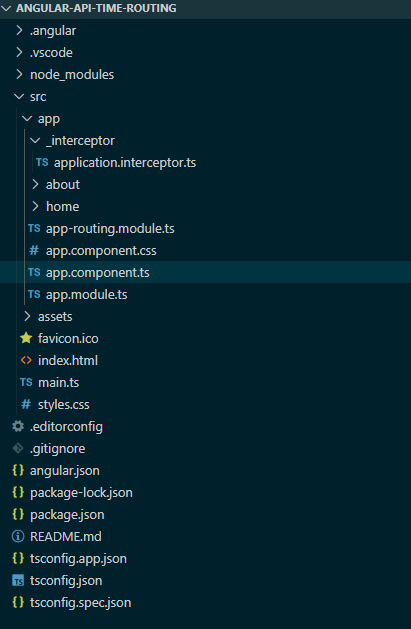 Folder Structure
Folder StructureDependencies
"dependencies": {
"@angular/animations": "^17.3.0",
"@angular/common": "^17.3.0",
"@angular/compiler": "^17.3.0",
"@angular/core": "^17.3.0",
"@angular/forms": "^17.3.0",
"@angular/platform-browser": "^17.3.0",
"@angular/platform-browser-dynamic": "^17.3.0",
"@angular/router": "^17.3.0",
"rxjs": "~7.8.0",
"tslib": "^2.3.0",
"zone.js": "~0.14.3"
}Example
JavaScript //app.module.ts import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common'; import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; import { ApplicationInterceptor } from './_interceptor/application.interceptor'; import { HTTP_INTERCEPTORS } from '@angular/common/http'; import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module'; @NgModule({ declarations: [AppComponent], imports: [ BrowserModule, CommonModule, AppRoutingModule, ], providers: [ { provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: ApplicationInterceptor, multi: true, }, ], bootstrap: [AppComponent], }) export class AppModule { } //app.component.ts import { Component, OnDestroy, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { Subscription } from 'rxjs'; import { Router, NavigationStart, NavigationEnd } from '@angular/router'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', template: ` <h1>Angular Routing and API Load Timing</h1> <nav><a routerLink="">Home</a> | <a routerLink="/about">About</a></nav> <router-outlet></router-outlet> <p> <span style="color: #333333; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px"> Navigation time: </span> <span style="color: #ff2222; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px" >{{ this.routingTotal }} ms</span > </p> `, styleUrl: './app.component.css', }) export class AppComponent implements OnInit, OnDestroy { title = 'angular-api-time-routing'; routerSubscription!: Subscription; routingStart!: number | null; routingEnd!: number | null; routingTotal!: number | null; constructor(private router: Router) { } ngOnInit(): void { this.routerSubscription = this.router.events.subscribe((event) => { if (event instanceof NavigationStart) { this.routingStart = performance.now(); this.routingEnd = null; } else if (event instanceof NavigationEnd) { this.routingEnd = performance.now(); if (this.routingStart !== null) { this.routingTotal = this.routingEnd - this.routingStart; console.log( `%c Navigation time: %c ${this.routingEnd - this.routingStart} ms`, `color: #CCCCCC; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px`, `color: #ff2222; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px` ); } } }); } ngOnDestroy() { if (this.routerSubscription) { this.routerSubscription.unsubscribe(); console.log('clear'); } } } //app-routing.module.ts import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router'; import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component'; import { AboutComponent } from './about/about.component'; const routes: Routes = [ { path: '', component: HomeComponent, pathMatch: 'full' }, { path: 'about', component: AboutComponent }, ]; @NgModule({ imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)], exports: [RouterModule], }) export class AppRoutingModule { } //application.interceptor.ts import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { HttpInterceptor, HttpRequest, HttpHandler, HttpEvent, } from '@angular/common/http'; import { Observable } from 'rxjs'; import { tap } from 'rxjs/operators'; @Injectable() export class ApplicationInterceptor implements HttpInterceptor { intercept( httpReq: HttpRequest<any>, httpNext: HttpHandler ): Observable<HttpEvent<any>> { const apiStart = performance.now(); return httpNext.handle(httpReq).pipe( tap(() => { const apiEnd = performance.now(); console.log( `%c API req name: %c ${httpReq.url}, %c API time: %c ${apiEnd - apiStart } ms`, `color: #CCCCCC; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px`, `color: #ff2222; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px`, `color: #CCCCCC; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px`, `color: #ff2222; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px` ); }) ); } } Output
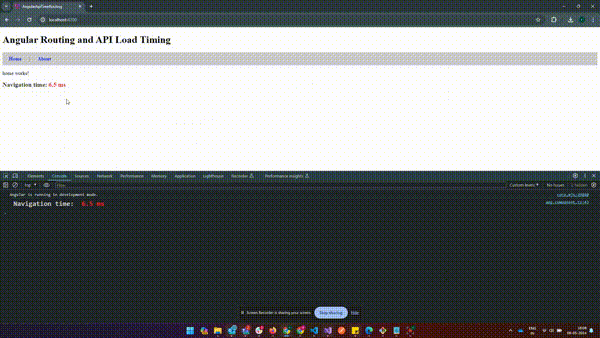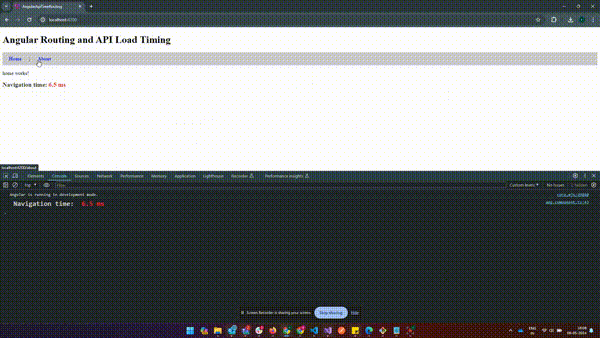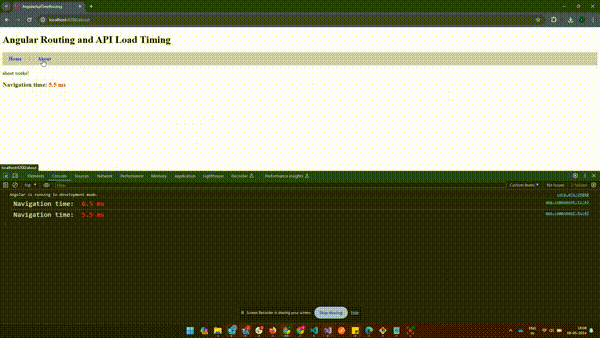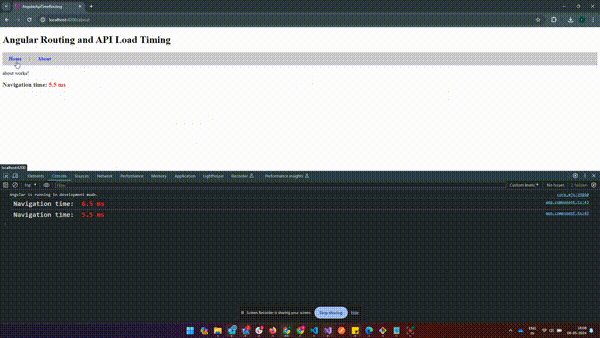 How to Get Page Load Time in Angular?
How to Get Page Load Time in Angular?The above example shows how to capture page load time including API calls after routing to a new URL.
Explore
AngularJS Basics
AngularJS Directives
AngularJS Filters
AngularJS Converting Functions
AngularJS Comparing Functions
AngularJS Questions
AngularJS Examples
2 min read
My Profile