Clone linked list with next and random pointer
Last Updated : 28 Dec, 2024
Given a linked list of size n where each node has two links: next pointer pointing to the next node and random pointer to any random node in the list. The task is to create a clone of this linked list.
[Naive Approach - 1] Using Hashing - O(2n) Time and O(2n) Space
The idea is to create a new node corresponding to each node in the original linked list and store the new nodes in a hash table. Now, again traverse the original linked list and update the next and random pointers of new nodes corresponding to every original node.
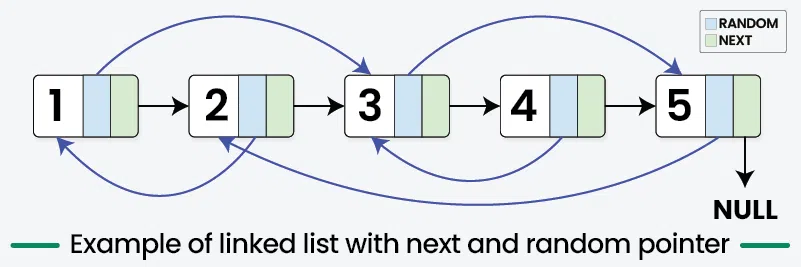
Illustration:
Steps to clone a linked list with next and random pointer:
- Create a hash table, say mp to store the new nodes corresponding to their original nodes.
- Traverse the original linked list and for every node, say curr,
- Create a new node corresponding to curr and push them into a hash table, mp[curr] = new Node().
- Again traverse the original linked list to update the next and random pointer of each new node, mp[curr]->next = mp[curr->next] and mp[curr]->random = mp[curr->random].
- Return mp[head] as the head of the cloned linked list.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++14 // C++ code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer using Hashing #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; Node* next; Node* random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = random = NULL; } }; // Function to clone the linked list Node* cloneLinkedList(Node* head) { // Map to store new nodes corresponding to // their original nodes unordered_map<Node*, Node*> mp; Node *curr = head; // Traverse original linked list to store new // nodes corresponding to original linked list while (curr != NULL) { mp[curr] = new Node(curr->data); curr = curr->next; } curr = head; // Loop to update the next and random pointers // of new nodes while (curr != NULL) { // Update the next pointer of new node mp[curr]->next = mp[curr->next]; // Update the random pointer of new node mp[curr]->random = mp[curr->random]; curr = curr->next; } // Return the head of the clone return mp[head]; } // Function to print the linked list void printList(Node* head) { while (head != NULL) { cout << head->data << "("; if(head->random) cout << head->random->data << ")"; else cout << "null" << ")"; if(head->next != NULL) cout << " -> "; head = head->next; } cout << endl; } int main() { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node* head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); head->random = head->next->next; head->next->random = head; head->next->next->random = head->next->next->next->next; head->next->next->next->random = head->next->next; head->next->next->next->next->random = head->next; // Print the original list cout << "Original linked list:\n"; printList(head); // Function call Node* clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); cout << "Cloned linked list:\n"; printList(clonedList); return 0; } // Java code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer using Hashing import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; // Define the Node class class Node { int data; Node next; Node random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; random = null; } } class GfG { // Function to clone the linked list static Node cloneLinkedList(Node head) { // Hash Map to store new nodes corresponding // to their original nodes Map<Node, Node> mp = new HashMap<>(); Node curr = head; // Traverse original linked list to store new nodes // corresponding to original linked list while (curr != null) { mp.put(curr, new Node(curr.data)); curr = curr.next; } curr = head; // Loop to update the next and random pointers // of new nodes while (curr != null) { // Update the next pointer of new node Node newNode = mp.get(curr); newNode.next = mp.get(curr.next); // Update the random pointer of new node newNode.random = mp.get(curr.random); curr = curr.next; } // Return the head of the clone return mp.get(head); } // Function to print the linked list static void printList(Node head) { while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.data + "("); if (head.random != null) System.out.print(head.random.data + ")"); else System.out.print("null" + ")"); if (head.next != null) System.out.print(" -> "); head = head.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list System.out.println("Original linked list:"); printList(head); // Function call Node clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); System.out.println("Cloned linked list:"); printList(clonedList); } } # Python code to Clone a linked list with next and random # pointer using Hashing class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None self.random = None # Function to clone the linked list def cloneLinkedList(head): # Dictionary to store new nodes corresponding # to their original nodes nodeMap = {} curr = head # Traverse original linked list to store new nodes # corresponding to original linked list while curr is not None: nodeMap[curr] = Node(curr.data) curr = curr.next curr = head # Loop to update the next and random pointers # of new nodes while curr is not None: newNode = nodeMap[curr] # Update the next pointer of new node newNode.next = nodeMap.get(curr.next) # Update the random pointer of new node newNode.random = nodeMap.get(curr.random) curr = curr.next # Return the head of the clone return nodeMap.get(head) def printList(head): curr = head while curr is not None: print(f'{curr.data}(', end='') if curr.random: print(f'{curr.random.data})', end='') else: print('null)', end='') if curr.next is not None: print(' -> ', end='') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Creating a linked list with random pointer head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head.random = head.next.next head.next.random = head head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next # Print the original list print("Original linked list:") printList(head) # Function call clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head) print("Cloned linked list:") printList(clonedList) // C# code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer using Hashing using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int Data; public Node Next; public Node Random; public Node(int x) { Data = x; Next = null; Random = null; } } class GfG { // Function to clone the linked list public static Node CloneLinkedList(Node head) { // Dictionary to store new nodes corresponding // to their original nodes Dictionary<Node, Node> mp = new Dictionary<Node, Node>(); Node curr = head; // Traverse original linked list to store new nodes // corresponding to original linked list while (curr != null) { mp[curr] = new Node(curr.Data); curr = curr.Next; } curr = head; // Loop to update the next and random pointers of new nodes while (curr != null) { Node newNode = mp[curr]; if(curr.Next != null) newNode.Next = mp[curr.Next]; newNode.Random = mp[curr.Random]; curr = curr.Next; } // Return the head of the clone return mp[head]; } // Function to print the linked list public static void PrintList(Node head) { while (head != null) { Console.Write(head.Data + "("); if (head.Random != null) Console.Write(head.Random.Data); else Console.Write("null"); Console.Write(")"); if (head.Next != null) Console.Write(" -> "); head = head.Next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.Next = new Node(2); head.Next.Next = new Node(3); head.Next.Next.Next = new Node(4); head.Next.Next.Next.Next = new Node(5); head.Random = head.Next.Next; head.Next.Random = head; head.Next.Next.Random = head.Next.Next.Next.Next; head.Next.Next.Next.Random = head.Next.Next; head.Next.Next.Next.Next.Random = head.Next; // Print the original list Console.WriteLine("Original linked list:"); PrintList(head); // Function call Node clonedList = CloneLinkedList(head); Console.WriteLine("Cloned linked list:"); PrintList(clonedList); } } // JavaScript code to Clone a linked list with next // and random pointer using Hashing class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } // Function to clone the linked list function cloneLinkedList(head) { // Map to store new nodes corresponding to // their original nodes const mp = new Map(); let curr = head; // Traverse original linked list to store new nodes // corresponding to original linked list while (curr !== null) { mp.set(curr, new Node(curr.data)); curr = curr.next; } curr = head; // Loop to update the next and random pointers // of new nodes while (curr !== null) { const newNode = mp.get(curr); newNode.next = mp.get(curr.next) || null; newNode.random = mp.get(curr.random) || null; curr = curr.next; } // Return the head of the clone return mp.get(head) || null; } // Function to print the linked list function printList(head) { let result = ""; while (head !== null) { result += head.data + "("; result += head.random ? head.random.data : "null"; result += ")"; if (head.next !== null) { result += " -> "; } head = head.next; } console.log(result); } // Creating a linked list with random pointer const head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list console.log("Original linked list:"); printList(head); // Function call const clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); console.log("Cloned linked list:"); printList(clonedList); OutputOriginal linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2) Cloned linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2)
Time Complexity: O(2n), as we are traversing the linked list twice.
Auxiliary Space: O(2n), extra O(n) space as we are using a hash table to store the new nodes.
[Naive Approach - 2] Using Hashing and Recursion- O(n) Time and O(3n) Space
The idea is to create a new node corresponding to each node in the original linked list and store the new nodes in a hash table. While traversing the original linked list we also use recursion to update the next and random pointers of new nodes corresponding to every original node.
For a more detailed solution and code checkout, this article Clone a linked list with next and random pointer using Recursion
Time Complexity: O(n) , where n is the number of nodes in linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(3n) , extra O(n) space as we are using a hash table to store the new nodes as well for recursion stack space.
[Expected Approach] By Inserting Nodes In-place - O(3n) Time and O(1) Space
The idea is to create duplicate of a node and instead of storing in a separate hash table, we can insert it in between the original node and the next node. Now, we will have new nodes at alternate positions.
Now for a node X its duplicate will be X->next and the random pointer of the duplicate should point to X->random->next (as that is the duplicate of X->random). So, iterate over the entire linked list to update the random pointer of all the cloned nodes and then iterate again to separate the original linked list and the cloned linked list.
Illustration:
Follow the steps mentioned below to implement the idea:
- Create the copy of node 1 and insert it between node 1 and node 2 in the original Linked List, create the copy of node 2 and insert it between 2nd and 3rd node and so on. Add the copy of N after the Nth node
- Connect the clone node by updating the random pointers.
- Separate the cloned linked list from the original list by updating the next pointers.
C++ // C++ code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; Node *next, *random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = random = NULL; } }; Node* cloneLinkedList(Node* head) { if (head == NULL) { return NULL; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to // the original nodes Node* curr = head; while (curr != NULL) { Node* newNode = new Node(curr->data); newNode->next = curr->next; curr->next = newNode; curr = newNode->next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != NULL) { if (curr->random != NULL) curr->next->random = curr->random->next; curr = curr->next->next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node* clonedHead = head->next; Node* clone = clonedHead; while (clone->next != NULL) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr->next = curr->next->next; clone->next = clone->next->next; // Move pointers of original as well as // cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr->next; clone = clone->next; } curr->next = NULL; clone->next = NULL; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list void printList(Node* head) { while (head != NULL) { cout << head->data << "("; if(head->random) cout << head->random->data << ")"; else cout << "null" << ")"; if(head->next != NULL) cout << " -> "; head = head->next; } cout << endl; } int main() { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node* head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); head->random = head->next->next; head->next->random = head; head->next->next->random = head->next->next->next->next; head->next->next->next->random = head->next->next; head->next->next->next->next->random = head->next; // Print the original list cout << "Original linked list:\n"; printList(head); // Function call Node* clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); cout << "Cloned linked list:\n"; printList(clonedList); return 0; } // Java code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { int data; Node next, random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = random = null; } } class GfG { // Function to clone the linked list static Node cloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.random != null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original and cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.data + "("); if (head.random != null) { System.out.print(head.random.data); } else { System.out.print("null"); } System.out.print(")"); if (head.next != null) { System.out.print(" -> "); } head = head.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list System.out.println("Original linked list:"); printList(head); // Function call Node clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); System.out.println("Cloned linked list:"); printList(clonedList); } } # Python code to Clone a linked list with next and random # pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None self.random = None # Function to clone the linked list def cloneLinkedList(head): if head is None: return None # Create new nodes and insert them next to # the original nodes curr = head while curr is not None: newNode = Node(curr.data) newNode.next = curr.next curr.next = newNode curr = newNode.next # Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head while curr is not None: if curr.random is not None: curr.next.random = curr.random.next curr = curr.next.next # Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head clonedHead = head.next clone = clonedHead while clone.next is not None: # Update the next nodes of original node # and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next clone.next = clone.next.next # Move pointers of original as well as # cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next clone = clone.next curr.next = None clone.next = None return clonedHead # Function to print the linked list def printList(head): while head is not None: print(f"{head.data}(", end="") if head.random: print(f"{head.random.data})", end="") else: print("null)", end="") if head.next is not None: print(" -> ", end="") head = head.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Creating a linked list with random pointer head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head.random = head.next.next head.next.random = head head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next # Print the original list print("Original linked list:") printList(head) # Function call clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head) print("Cloned linked list:") printList(clonedList) // C# code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int Data; public Node Next, Random; public Node(int x) { Data = x; Next = Random = null; } } public class GfG { public static Node CloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) return null; // Create new nodes and insert them next to // the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.Data); newNode.Next = curr.Next; curr.Next = newNode; curr = newNode.Next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.Random != null) curr.Next.Random = curr.Random.Next; curr = curr.Next.Next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.Next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.Next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.Next = curr.Next.Next; clone.Next = clone.Next.Next; // Move pointers of original as well as // cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.Next; clone = clone.Next; } curr.Next = null; clone.Next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list public static void PrintList(Node head) { while (head != null) { Console.Write(head.Data + "("); if (head.Random != null) Console.Write(head.Random.Data + ")"); else Console.Write("null)"); if (head.Next != null) Console.Write(" -> "); head = head.Next; } Console.WriteLine(); } public static void Main() { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.Next = new Node(2); head.Next.Next = new Node(3); head.Next.Next.Next = new Node(4); head.Next.Next.Next.Next = new Node(5); head.Random = head.Next.Next; head.Next.Random = head; head.Next.Next.Random = head.Next.Next.Next.Next; head.Next.Next.Next.Random = head.Next.Next; head.Next.Next.Next.Next.Random = head.Next; // Print the original list Console.WriteLine("Original linked list:"); PrintList(head); Node clonedList = CloneLinkedList(head); Console.WriteLine("Cloned linked list:"); PrintList(clonedList); } } // JavaScript code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } function cloneLinkedList(head) { if (head === null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the // original nodes let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { let newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr !== null) { if (curr.random !== null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; let clonedHead = head.next; let clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next !== null) { // Update the next nodes of original node and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original as well as cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list function printList(head) { let result = ""; while (head !== null) { result += head.data + "("; result += head.random ? head.random.data : "null"; result += ")"; if (head.next !== null) { result += " -> "; } head = head.next; } console.log(result); } // Creating a linked list with random pointer let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list console.log("Original linked list:"); printList(head); let clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); console.log("Cloned linked list:"); printList(clonedList); OutputOriginal linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2) Cloned linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2)
Time Complexity: O(3n), because we are traversing the linked list three times.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as we are storing all the cloned nodes in the original linked list itself, no extra space is required.
Similar Reads
Clone a linked list with next and random pointer in O(1) space Given a linked list of size N where each node has two links: next pointer pointing to the next node and random pointer to any random node in the list. The task is to create a clone of this linked list in O(1) space, i.e., without any extra space. Examples: Input: Head of the below linked listOutput:
10 min read
Clone linked list with next and random pointer using Recursion Given a linked list of size n where each node has two links: next pointer pointing to the next node and random pointer to any random node in the list. The task is to create a clone of this linked list.Approach :The idea is to create a new node corresponding to each node in the original linked list a
7 min read
Javascript Program For Cloning A Linked List With Next And Random Pointer- Set 2 We have already discussed 2 different ways to clone a linked list. In this post, one more simple method to clone a linked list is discussed.The idea is to use Hashing. Below is an algorithm. Traverse the original linked list and make a copy in terms of data.Make a hash map of key-value pair with the
3 min read
Javascript Program For Cloning A Linked List With Next And Random Pointer In O(1) Space Given a linked list having two pointers in each node. The first one points to the next node of the list, however, the other pointer is random and can point to any node of the list. Write a program that clones the given list in O(1) space, i.e., without any extra space. Examples: Input : Head of the
4 min read
Clone a Binary Tree with Random Pointers Given a Binary Tree where every node has data, a next pointer, a right pointer, and a random pointer. The random pointer points to any random node of the binary tree and can even point to NULL, the task is to clone the given binary tree.Example: Approach:The idea is to use hashmap to store mapping f
11 min read
Select a Random Node from a Singly Linked List Given a singly linked list, select a random node from the linked list (the probability of picking a node should be 1/N if there are N nodes in the list). You are given a random number generator.Below is a Simple Solution Count the number of nodes by traversing the list. Traverse the list again and s
14 min read