How to Clone All Branches in Git
- Git Clone All Branches
- Use the
git cloneCommand to Clone All Branches in Git - Use the
--mirrorOption to Clone All Branches in Git - Use the
--bareOption to Clone All Branches in Git

While developing software with the Git tool, you can create different branches for different features.
This article will explain how to clone all different branches from remote to local in Git.
Git Clone All Branches
When using the Git tool, you may need to use and track different branches. These branches are not automatically cloned when you download the master.
The rest of the article will explain how to clone all different branches from remote to local in different ways.
Use the git clone Command to Clone All Branches in Git
Clone your repository with the git clone command. Then navigate to the directory where your project is located.
git clone git://gitwebsite.com/user/test.git cd test Use the git branch command to view local branches. This command will only show you local branches.
git branch Use the branch command with the -a parameter. So, you can see other remote branches.
git branch -a 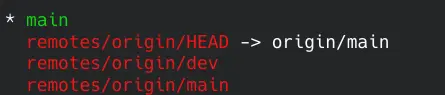
The git checkout command updates the files in the working tree according to the specified branch. Use the checkout command to work on one of these remote branches.
This command will create a local clone of the branch and switch to it. You can repeat it for all branches.
git checkout dev 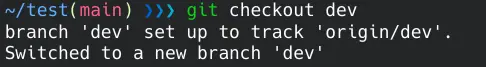
Use the git branch command again. You will see this branch as well.
Use the --mirror Option to Clone All Branches in Git
Create an empty directory and navigate to it. Clone your repository with the git clone --mirror command.
The --mirror option sets up a mirror of the source repository with all branches.
mkdir test cd test git clone --mirror git://gitwebsite.com/user/test.git .git The local repository inside the test directory seems empty. However, there is a hidden .git folder, and we can see it with the ls -a command in the terminal.
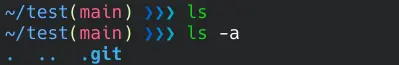
This command sets up the repository as a bare repository. To turn it back into a regular repository, change the bare Boolean value of git config to false.
git config --bool core.bare false Set HEAD with the git reset command. It gets everything from the current folder and creates all the branches on the local machine.
git reset --hard Use the git branch command. You will see all the branches.
git branch Use the --bare Option to Clone All Branches in Git
Create an empty directory and navigate to it. Use the git clone command with the --bare option.
mkdir test cd test git clone --bare git://gitwebsite.com/user/test.git .git The local repository inside the test directory seems empty. However, there is a .git folder, and we can see it with the ls -a command in the terminal.

This command sets up the repository as a bare repository. To turn it back into a regular repository, change the bare Boolean value of git config to false.
git config --bool core.bare false Set HEAD with the git reset command. It gets everything from the current folder and creates all the branches on the local machine.
git reset --hard Use the git branch command. You will see all branches.
git branch The --bare option and the --mirror option are the same. Compared to --bare, --mirror maps local branches of the source to local branches of the target and maps all refs (including remote-tracking branches, notes, etc.).
It sets up a refspec configuration such that all these refs are overwritten by a git remote update in the target repository.
Yahya Irmak has experience in full stack technologies such as Java, Spring Boot, JavaScript, CSS, HTML.
LinkedIn