Python math - hypot() Function
The Python math.hypot() function returns the length of the vector from the origin to the point given by arguments. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
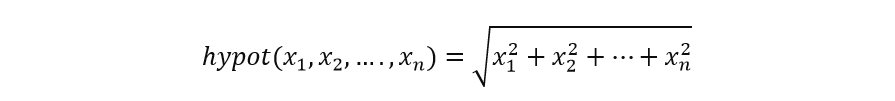
Note: In version 3.8 and later, the support for n-dimensional point is added. Formerly, only two dimensional point was supported.
Syntax
#Before version 3.8 math.hypot(x1, x2) #From version 3.8 math.hypot(*args)
Parameters
x1 | Required. Specify a value. |
x2 | Required. Specify a value. |
*args | Required. Specify the variable number of values separated by comma , specifying co-ordinates of n-dimensional point. |
Return Value
Returns sqrt(x2 +y2).
Example:
In the example below, hypot() function returns sqrt(x2 +y2).
import math print(math.hypot(3, 4)) print(math.hypot(5, 12)) print(math.hypot(8, 15))
The output of the above code will be:
5.0 13.0 17.0
Example:
The hypot() function can be used to calculate the length of the vector for multi-dimensional point also. Please note that this feature is added in version 3.8.
import math print(math.hypot(3, 4, 5))
The output of the above code will be:
7.0710678118654755
❮ Python Math Module


