Applications running on an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance can dynamically query instance metadata through the metadata service, such as instance IDs and IP addresses. This avoids hard-coding this information. To prevent metadata exposure from Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) attacks, we recommend accessing metadata using security hardening mode, which requires first getting an access token. Configure your instances to allow access only in this mode to effectively mitigate the security risks associated with normal mode.
Get instance metadata
Instance metadata is a collection of instance attributes, including key properties such as instance ID, network environment, and access credentials.
Method 1: Security hardening mode (recommended)
To access metadata in security hardening mode, you must first obtain a temporary access token. Then, you can include the token in your request to retrieve the metadata.
Linux
Log on to the instance.
Obtain a temporary token.
TOKEN=`curl -X PUT "http://100.100.100.200/latest/api/token" -H "X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token-ttl-seconds:21600"`The X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token-ttl-seconds parameter specifies the time-to-live (TTL) of the token in seconds. The value can range from 1 to 21600.
Include the token in your request to retrieve metadata.
curl -H "X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token: $TOKEN" http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/instance-idThe
instance-idat the end of the command retrieves the instance ID. You can replace it with other metadata items that you need to retrieve, such as mac (to retrieve the MAC address) or hostname (to retrieve the hostname).If the command is successful, the terminal outputs only the instance ID string, for example,
i-bp1******.
Windows
Log on to the instance.
Obtain a temporary token.
$token = Invoke-RestMethod -Headers @{"X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token-ttl-seconds" = "21600"} -Method PUT -Uri http://100.100.100.200/latest/api/tokenThe X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token-ttl-seconds parameter specifies the TTL of the token in seconds. The value can range from 1 to 21600.
Include the token in your request to retrieve metadata.
Invoke-RestMethod -Headers @{"X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token" = $token} -Method GET -Uri http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/instance-idThe
instance-idat the end of the command retrieves the instance ID. You can replace it with other metadata items that you need to retrieve, such as mac (to retrieve the MAC address) or hostname (to retrieve the hostname).If the command is successful, the terminal outputs only the instance ID string, for example,
i-bp1******.
Method 2: Normal mode
Normal mode is an insecure access method and is not recommended.
Linux:
# Send a GET request to get the instance ID. curl http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/instance-idWindows:
# Send a GET request to get the instance ID. Invoke-RestMethod -Uri http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/instance-id -Method Get
Enable access in security hardening mode only
To prevent serious security risks, enable Security Hardening Mode for your ECS instances. After this mode is enabled, you can access metadata only in security hardening mode. Any attempt to access metadata in normal mode returns a 403 - Forbidden error. By default, ECS instances allow token-free access to metadata (normal mode), which poses a high risk of SSRF attacks.
A typical attack scenario involves exploiting an application feature, such as downloading an image from an external URL. An attacker can craft a malicious request that tricks the server into accessing the internal metadata service on their behalf. This can be used to steal the temporary access credentials of the RAM role that is attached to the instance. If the role has high-level permissions, the attacker could gain control over your cloud resources or even take over your entire Alibaba Cloud account.
Enable security hardening mode when you create a new instance
Console
When you create an instance, set to Security Hardening Mode.
If the Security Hardening Mode option is not available when you create an instance from a custom image, you must upgrade the image.
CLI
When you create an instance by calling the RunInstances or CreateInstance operation, you can set the metadata access mode of the instance to security hardening mode by setting HttpEndpoint=enabled and HttpTokens=required. The following command is an example:
This command creates a Linux instance that runs only in security hardening mode.
aliyun ecs RunInstances \ --region cn-hangzhou \ --RegionId 'cn-hangzhou' \ --ImageId 'aliyun_3_x64_20G_alibase_20250629.vhd' \ --InstanceType 'ecs.g7.large' \ --VSwitchId 'vsw-bp1******trg' \ --SecurityGroupId 'sg-bp1******dgl' \ --SystemDisk.Size 40 \ --SystemDisk.Category cloud_essd \ --HttpEndpoint enabled \ --HttpTokens requiredAPI
When you create an instance by calling the RunInstances or CreateInstance operation, set the metadata access policy of the instance to security hardening mode by setting HttpEndpoint=enabled and HttpTokens=required.
Upgrade an existing instance to security hardening mode
Applicability
Windows instances: Do not support Security Hardening Mode. If you force this mode, instance initialization fails and key functions such as hostname modification and KMS activation are affected.
Linux instances: These instances support the upgrade. However, you must complete the dependency checks and modifications described in the following sections before you perform the upgrade.
Step 1: Check and upgrade code and dependencies
Before you switch to Security Hardening Mode, the instance and all applications that are deployed on it must meet the following requirements:
Make sure that the Cloud-init version is 23.2.2 or later. You can log on to the instance and run the
cloud-init --versioncommand to check the current version. If the version is earlier than 23.2.2, the instance fails to start after you switch to security hardening mode. You must first upgrade Cloud-init to version 23.2.2 or later.All application code and scripts must access instance metadata using Method 1: Security hardening mode.
ImportantIf your application code depends on the Credentials library to obtain a Security Token Service (STS) token for SDK configuration, upgrade the Credentials dependency to a version that supports security hardening mode.
After you complete the upgrades, check whether the ECS instance is being accessed in normal mode. For more information, see How do I detect if an ECS instance is being accessed in normal mode?. After you confirm that no normal mode access exists, enable Security Hardening Mode for the instance.
Step 2: Switch to security hardening mode
Console
Go to the ECS console - Instances page and select a region and a resource group.
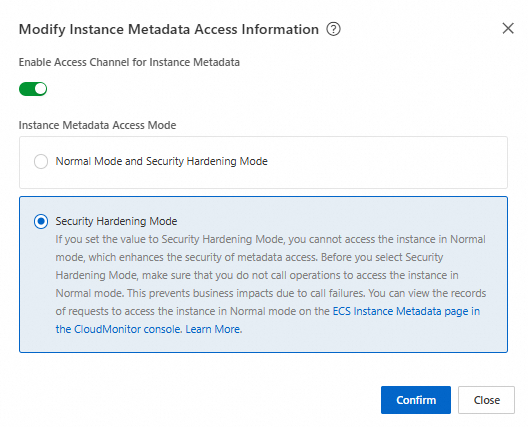
In the Actions column, click .
Turn on the Enable Instance Metadata Access Channel switch, set Instance Metadata Access Mode to Security Hardening Mode, and then click OK.
CLI
Call the ModifyInstanceMetadataOptions operation and set HttpEndpoint=enabled and HttpTokens=required to switch the instance metadata access mode to Security Hardening Mode. The following command is an example:
aliyun ecs ModifyInstanceMetadataOptions \ --region cn-hangzhou \ --RegionId 'cn-hangzhou' \ --InstanceId 'i-bp1******ke' \ --HttpEndpoint enabled \ --HttpTokens requiredAPI
Call the ModifyInstanceMetadataOptions operation and set HttpEndpoint=enabled and HttpTokens=required to switch the instance metadata access mode to Security Hardening Mode.
After you switch modes, continuously monitor the metadata access and application status of the instance to ensure business continuity. This helps prevent service interruptions caused by applications that have not been modified. If an issue occurs, switch back to Normal And Security Hardening Modes to prioritize service recovery. Then, perform Step 1: Check and upgrade code and dependencies again.
Instance metadata details
Category | Metadata | Description | Example |
Basic instance information |
| The instance ID. |
|
| The instance name. |
| |
| The hostname of the instance. |
| |
| The instance type. |
| |
| The serial number of the instance. |
| |
| The ID of the region where the instance resides. |
| |
| The zone where the instance resides. |
| |
| The Alibaba Cloud account ID of the instance owner. |
| |
Image information |
| The ID of the image that was used to create the instance. |
|
| The product code of the Alibaba Cloud Marketplace image. |
| |
| The billing method of the Alibaba Cloud Marketplace image. |
| |
| The image repository address, such as a yum or apt source, that the package manager of the Linux instance uses to obtain updates. |
| |
Basic network configuration |
| The network type. Only VPC-type instances are supported. |
|
| The ID of the VPC where the instance resides. |
| |
| The CIDR block of the VPC where the instance resides. |
| |
| The ID of the virtual switch where the instance resides. |
| |
| The CIDR block of the virtual switch where the instance resides. |
| |
| The maximum outbound internal bandwidth of the instance type. Unit: Kbit/s. |
| |
| The DNS configuration of the instance. |
| |
| The NTP server address. |
| |
Primary ENI IP addresses |
| The MAC address of the instance. If the instance has multiple network interface cards, only the MAC address on eth0 is displayed. |
|
| The private IPv4 address of the primary Elastic Network Interface (ENI) of the instance. |
| |
| The public IPv4 address of the primary ENI of the instance. |
| |
| The static public IPv4 address of the instance or the Elastic IP Address that is attached to the primary ENI. |
| |
Elastic network interface details |
| The ID of the ENI. Replace the [mac] parameter with the MAC address of the instance. You can obtain the MAC address from the mac metadata item. The same applies to the following items. |
|
| The ID of the VPC where the ENI resides. |
| |
| The ID of the virtual switch where the ENI resides. |
| |
| The primary private IP address of the ENI. |
| |
| The list of private IPv4 addresses that are assigned to the ENI. |
| |
| The list of private IPv4 prefixes that are assigned to the ENI. |
| |
| The subnet mask of the ENI. |
| |
| The IPv4 gateway address of the ENI. |
| |
| The IPv4 CIDR block of the virtual switch where the ENI resides. |
| |
| The IPv4 CIDR block of the VPC where the ENI resides. |
| |
| The list of IPv6 addresses that are assigned to the ENI. This parameter is supported only for VPC-type instances for which IPv6 is configured. |
| |
| The list of IPv6 prefixes that are assigned to the ENI. |
| |
| The IPv6 gateway address of the VPC where the ENI resides. |
| |
| The IPv6 CIDR block of the virtual switch where the ENI resides. This parameter is supported only for VPC-type instances for which IPv6 is configured. |
| |
| The IPv6 CIDR block of the VPC where the ENI resides. This parameter is supported only for VPC-type instances for which IPv6 is configured. |
| |
Disk information |
| The disk serial number. |
|
| The disk ID. |
| |
| The disk name. |
| |
Security and credentials |
| The public key. This parameter is available only if a public key was provided when the instance was launched. |
|
| The temporary security credentials of the RAM role that is associated with the instance. Replace [role-name] with the name of the RAM role. The credentials expire at the time specified in the Expiration field. You must call the operation again to obtain new credentials. | | |
Advanced instance attributes |
| The ECS virtualization solution. Virt 1.0 and Virt 2.0 are supported. |
|
| The internal build number. |
| |
| The stop and release time that is set by the operating system for a spot instance. The time is in UTC+0 and the format is yyyy-MM-ddThh:mm:ssZ. |
| |
Windows-specific configuration |
| The KMS activation server for Windows instances. |
|
| The update server for Windows instances. |
| |
| The update status monitoring server for Windows instances. |
|
FAQ
What is an SSRF attack, and how does security hardening mode defend against it?
SSRF is a security vulnerability where an attacker tricks a server into making unauthorized network requests. This can be used to access protected internal systems such as the metadata service or databases. For example, an attacker can submit a URL that contains
http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/to trick an application into fetching and returning sensitive information from the metadata. This causes a data breach.By default, ECS instances allow token-free access to metadata (normal mode). Enabling security hardening mode enforces a token validation mechanism. The client must first send a PUT request to obtain a temporary token and then include that token in subsequent GET requests. Because SSRF attacks cannot easily initiate PUT requests, they cannot obtain a token. This effectively blocks access and improves metadata security.
I cannot access instance metadata using commands in security hardening mode. How do I fix this?
The following command errors are common:
The TTL of the instance metadata access credential is out of range (400 - Missing or Invalid Parameters)
The TTL for an instance metadata access credential is 1 to 21,600 seconds. If the value exceeds this limit, a 400 - Missing or Invalid Parameters error is returned.
curl -X PUT "http://100.100.100.200/latest/api/token" -H "X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token-ttl-seconds: 21700"The request contains the X-Forwarded-For header (403 - Forbidden)
curl -X PUT "http://100.100.100.200/latest/api/token" -H "X-Forwarded-For: www.ba****.com"The specified instance metadata access credential is invalid (401 - Unauthorized)
curl -H "X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token: aaa" -v http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/
What do I do if my high-frequency access to the metadata service is throttled?
The metadata service has access frequency limits. A best practice is to retrieve metadata items that rarely change, such as instance-id, once at application startup. Then, cache them in local memory or a file with a reasonable time-to-live.
My application stopped working after I changed the instance metadata access mode to security hardening mode. How do I troubleshoot this issue?
An application or script on the instance may still be using normal mode. Follow the steps in Upgrade an existing instance to security hardening mode to check for and upgrade any applications that use normal mode.
Can I access the metadata address from a local host?
No, you cannot. The address
100.100.100.200is a link-local address that is reachable only from within an ECS instance over its virtual network interface. Any request sent to this address from outside the instance cannot be routed. This is a fundamental design principle for ensuring metadata security.What do I do if I cannot select security hardening mode when I create an instance from a custom image?
When you create an ECS instance from a custom Linux image, you may find that you cannot select or enable Security Hardening Mode. This usually means that the image does not meet the requirements for this security feature. To resolve this issue, upgrade the image as follows:
Create a temporary instance: Use the custom image that you want to upgrade to create a temporary ECS instance for diagnostics and modification.
Modify the temporary instance: On the temporary instance that you created in Step 1, perform the following modifications. For more information, see Upgrade an existing instance to security hardening mode.
Upgrade Cloud-init: Upgrade Cloud-init to version 23.2.2 or later.
Modify applications and scripts: Modify all applications or scripts that use normal mode to adapt them to security hardening mode.
Create a new image and modify its attributes: After you complete the modifications, create a new custom image from the instance. Then, call the ModifyImageAttribute operation to set the
Features.ImdsSupportattribute of the image to `v2`.Release resources: After the new image is created, promptly release the temporary instance to save costs.
Which versions of the Credentials tool support security hardening mode?
Earlier versions of Credentials do not support access to metadata in security hardening mode. If you switch to security hardening mode, these versions cannot obtain an STS token from the metadata in normal mode to initialize the SDK. This causes service interruptions.
Before you switch modes, upgrade the Credentials dependency to a version that supports security hardening mode. The version requirements are as follows:
Java: credentials-java version >=
0.3.10.Node.js: credentials version >=
2.3.1.PHP: credentials version >=
1.2.0.Python: alibabacloud_credentials version >=
0.3.6.Go: credentials-go version >=
1.3.10.
How do I detect if an ECS instance is being accessed in normal mode?
When you check for application code on an instance that uses normal mode, you can use the following methods to detect and locate the specific processes. This helps you perform the required upgrades.
Method 1: Use CloudMonitor to check for normal mode access
You can check the ECS metadata monitoring data in the CloudMonitor console to quickly confirm whether the instance has been recently accessed in normal mode.
Log on to the CloudMonitor console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Then, search for and go to the ECS Metadata monitoring page.
View the Successful Normal Mode Accesses metric for the target instance.
If the value of this metric is not 0, the instance is being accessed in normal mode. You must find the applications that use this mode and upgrade them to use security hardening mode.
Method 2: Use a Cloud Assistant plugin to locate a specific process
You can use a Cloud Assistant plugin to help you accurately locate the processes within an instance that are using normal mode to access metadata.
Supported operating systems
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 Pro
Anolis OS 8
CentOS Stream 8/9
CentOS 8
Ubuntu: 20/24
Debian:10,11,12
Fedora 35+
AlmaLinux 8/9
Rocky Linux 8/9
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8/9
For Red Hat, you must download an RPM package to install Cloud Assistant Agent.
SUSE 15.1/15.2/15.3/15.4/15.5/15.6
OpenSuse 15.2/15.3/15.4/15.5/15.6
Procedure
Install and enable the Cloud Assistant plugin
Log on to the ECS instance and run the following commands to install and start the monitoring service. After this service is enabled, it consumes some instance resources.
# Deploy the monitoring service. sudo acs-plugin-manager --exec --plugin ACS-ECS-ImdsPacketAnalyzer # Check the status of the monitoring service. sudo systemctl status imds_tracer_tool
Locate the problematic process Run the command to check which processes are still accessing metadata in normal mode. The log displays the process IDs (PIDs) of the relevant processes.
cat /var/log/imds/imds-trace.* | grep WARNING
Analyze and modify Based on the PIDs in the log, find the corresponding applications or scripts and upgrade them to access metadata in security hardening mode.