You can enable Auto Mode when you create an ACK managed cluster. This mode lets you create a best-practice Kubernetes cluster with a single click after completing simple planning and configuration. By default, the cluster creates an Auto Mode node pool, and ACK manages the lifecycle and O&M of the nodes in this pool.
Before you enable Auto Mode, see Introduction to Auto Mode to learn about its features and scenarios.
Preparations
Planning and design
Before you create a cluster, plan the cluster configurations based on your requirements. This helps ensure that the cluster runs in a stable, efficient, and secure manner.
Region: Services deployed in a region that is geographically closer to your users are more responsive when your users access the services.
Zone: We recommend that you configure multiple zones to ensure high availability of the cluster.
Plan the network of an ACK cluster: Configure the virtual private cloud (VPC) CIDR block, vSwitch CIDR block, container CIDR block, and Service CIDR block based on your business scenario and cluster size. Then, specify the IP address range of the cluster and the number of available IP addresses for pods and nodes.
Access to Internet: Specifies whether the nodes in the cluster can access the Internet. The cluster must have Internet when pulling public images.
Activation and authorization
Before you create a cluster, make sure that you have activated ACK, granted the required ACK service roles to your Alibaba Cloud account or RAM user, and activated related cloud products, such as VPC, Server Load Balancer (SLB), and NAT Gateway.
Activate ACK: If this is your first time using ACK, log on to the ACK activation page and follow the on-screen instructions to activate the service.
Grant permissions: Go to the RAM console for quick authorization page to grant the default service roles to your Alibaba Cloud account. This ensures that ACK can access the required cloud resources.
Activate related cloud products: Activate the cloud products that ACK clusters depend on, such as VPC and SLB.
NoteThe creation process involves purchasing pay-as-you-go resources, such as Classic Load Balancer (CLB). Make sure that your account has a sufficient balance to prevent service interruptions due to overdue payments.
Only Alibaba Cloud accounts can activate cloud products. To authorize a Resource Access Management (RAM) user to manage activated cloud products, see Use RAM to grant access permissions on clusters and cloud resources.
Procedure
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
In the navigation bar on the top, select the resource group and region where your target resource resides.
On the Clusters page, click Create Cluster. On the ACK Managed Cluster page, turn on the Auto Mode switch.
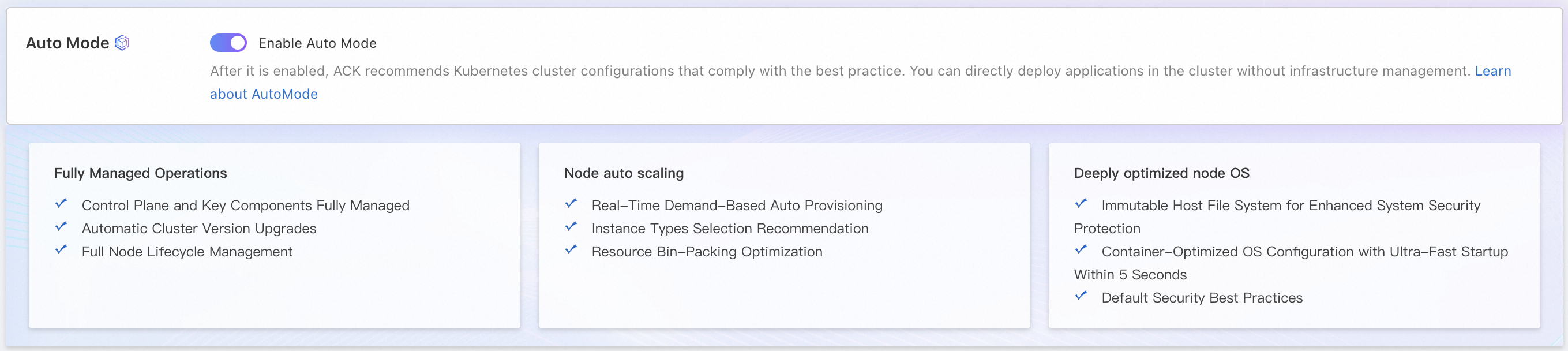
For more information about the parameters, see Configuration description. Follow the on-screen instructions to configure the cluster. Carefully review the cluster configurations, read the terms of service, and then click Create Cluster.
Auto Mode is available only for ACK Pro clusters. It incurs fees for cluster management and related cloud products. You can view the total cluster cost at the bottom of the creation page. You can also view the billing documentation for ACK and other products. For more information, see Billing overview and Cloud resource fees.
You can also click Equivalent Code in the upper-right corner of the page to generate sample Terraform or software development kit (SDK) parameters that correspond to the current cluster configuration.
After the cluster is created, an Auto Mode node pool is automatically created. For more information, see Auto Mode node pools. This node pool dynamically scales in or out based on the workload. ACK manages the node lifecycle and is responsible for O&M tasks such as OS version upgrades, software version upgrades, and security vulnerability fixes.
After the cluster is created, ACK installs components based on your configurations. These components may consume computing resources in the cluster. The Auto Mode node pool automatically scales out to provide the required nodes.
Configuration description
You can create a cluster with the default configurations or adjust them based on your requirements and available resources. In the Modifiable column of the following tables, ![]() indicates that the configuration cannot be modified after the cluster is created, and
indicates that the configuration cannot be modified after the cluster is created, and ![]() indicates that it can be modified. Pay close attention to the items that cannot be modified.
indicates that it can be modified. Pay close attention to the items that cannot be modified.
Network configurations
Configuration item | Description | Modifiable |
IPv6 Dual-stack | If you enable IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack, a dual-stack cluster is created. Important
| ✗ |
VPC | Configure the VPC of the cluster. You can specify a zone to automatically create a VPC. You can also select an existing VPC in the VPC list. | ✗ |
Configure SNAT for VPC | Do not select this option if you use a shared VPC for the cluster. After you select this check box, ACK performs the following operations on the newly created or selected VPC:
If you do not select this check box, you can manually configure a NAT gateway and configure SNAT rules after creating the cluster to ensure that instances in the VPC can access the Internet. For more information, see Create and manage an Internet NAT gateway. | ✓ |
Access to API Server | The API server provides various HTTP REST interfaces for managing resource objects (such as pods and Services), including create, read, update, delete, and watch operations.
Specify whether to Expose API server with EIP:
Important
| ✗ |
Network Plug-in | Flannel and Terway are supported. For more information about the comparison between Terway and Flannel, see Comparison between Terway and Flannel.
| ✗ |
Pod vSwitch | Configure this parameter only if you select Terway as the network plug-in. The vSwitch that is used to assign IP addresses to pods. Each pod vSwitch corresponds to a vSwitch of a worker node. The vSwitch of the pod and the vSwitch of the worker node must be in the same zone. Important We recommend that you set the subnet mask of the CIDR block of a pod vSwitch to no longer than 19 bits, but the subnet mask must not exceed 25 bits. Otherwise, the cluster network has only a limited number of IP addresses that can be allocated to the pods. As a result, the cluster may not function as expected. | ✓ |
Container CIDR Block | Configure this parameter only if you select Flannel as the network plug-in. The container CIDR block must not overlap with the CIDR block of the VPC, the CIDR blocks of the ACK clusters in the VPC, or the Service CIDR block. The container CIDR block cannot be modified after it is specified. For more information about how to plan CIDR blocks for a cluster, see Network planning of an ACK managed cluster. | ✗ |
Number of Pods per Node | Configure this parameter only if you select Flannel as the network plug-in. The maximum number of pods that can be stored on a single node. | ✗ |
Service CIDR | Specify the CIDR block of Services in the cluster. The Service CIDR block must not overlap with the CIDR block of the VPC, the CIDR blocks of the ACK clusters in the VPC, or the pod CIDR block. The Service CIDR block cannot be modified after it is specified. For more information about how to plan CIDR blocks for a cluster, see Network planning of an ACK managed cluster. | ✗ |
Service Forwarding Mode | iptables and IP Virtual Server (IPVS) are supported.
| ✗ |
Advanced Options
What to do next
References
Shared responsibility model
The Auto Mode of an ACK managed cluster provides automated and intelligent O&M features for Kubernetes clusters to reduce your O&M workload. However, you are still responsible for certain tasks in some scenarios.
Alibaba Cloud responsibilities | Customer responsibilities | Shared responsibilities |
|
|
|
Quotas and limits
If the cluster size is large or the account has a large number of resources, follow the quotas and limits specified for ACK clusters. For more information, see Quotas and limits.
Limits: ACK configuration limits, such as account balance and capacity limit of a cluster, which is the maximum capacity of different Kubernetes resources in a cluster.
Quota limits and how to increase quotas: Quota limits for ACK clusters and the quota limits of cloud services that ACK depends on, such as ECS or VPC. If you want to increase the quota, see the related topics.