UVM TestBecnh example code
Table of Contents
UVM TestBench to verify Memory Model
For Design specification and Verification plan, refer to Memory Model.
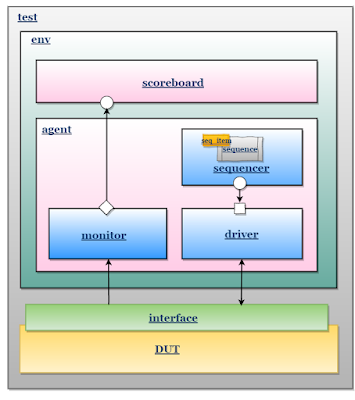
To maintain uniformity in naming the components/objects, all the component/object name’s are starts with mem_*.
TestBench Components/Objects
Sequence item
- fields required to generate the stimulus are declared in the sequence_item.
- sequence_item can be used as a placeholder for the activity monitored by the monitor on DUT signals.
1. sequence_item is written by extending uvm_seq_item;
class mem_seq_item extends uvm_sequence_item; //Utility macro `uvm_object_utils(mem_seq_item) //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_seq_item"); super.new(name); endfunction endclass
2. Declaring the fields in mem_seq_item,
class mem_seq_item extends uvm_sequence_item; //data and control fields bit [3:0] addr; bit wr_en; bit rd_en; bit [7:0] wdata; bit [7:0] rdata; //Utility macro `uvm_object_utils(mem_seq_item) //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_seq_item"); super.new(name); endfunction endclass
3. To generate the random stimulus, declare the fields as rand.
class mem_seq_item extends uvm_sequence_item; //data and control fields rand bit [3:0] addr; rand bit wr_en; rand bit rd_en; rand bit [7:0] wdata; bit [7:0] rdata; //Utility macro `uvm_object_utils(mem_seq_item) //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_seq_item"); super.new(name); endfunction endclass
4. In order to use the uvm_object methods ( copy, compare, pack, unpack, record, print, and etc ),
all the fields are registered to uvm_field_* macros.
class mem_seq_item extends uvm_sequence_item; //data and control fields rand bit [3:0] addr; rand bit wr_en; rand bit rd_en; rand bit [7:0] wdata; bit [7:0] rdata; //Utility and Field macros, `uvm_object_utils_begin(mem_seq_item) `uvm_field_int(addr,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_field_int(wr_en,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_field_int(rd_en,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_field_int(wdata,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_object_utils_end //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_seq_item"); super.new(name); endfunction endclass
5. Either write or read operation will be performed at once, so the constraint is added to generate wr_en and rd_en.
class mem_seq_item extends uvm_sequence_item; //data and control fields rand bit [3:0] addr; rand bit wr_en; rand bit rd_en; rand bit [7:0] wdata; bit [7:0] rdata; //Utility and Field macros, `uvm_object_utils_begin(mem_seq_item) `uvm_field_int(addr,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_field_int(wr_en,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_field_int(rd_en,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_field_int(wdata,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_object_utils_end //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_seq_item"); super.new(name); endfunction //constaint, to generate any one among write and read constraint wr_rd_c { wr_en != rd_en; }; endclass Complete mem_seq_item code,
class mem_seq_item extends uvm_sequence_item; //data and control fields rand bit [3:0] addr; rand bit wr_en; rand bit rd_en; rand bit [7:0] wdata; bit [7:0] rdata; //Utility and Field macros, `uvm_object_utils_begin(mem_seq_item) `uvm_field_int(addr,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_field_int(wr_en,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_field_int(rd_en,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_field_int(wdata,UVM_ALL_ON) `uvm_object_utils_end //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_seq_item"); super.new(name); endfunction //constaint, to generate any one among write and read constraint wr_rd_c { wr_en != rd_en; }; endclass Sequence
- Sequence generates the stimulus and sends to driver via sequencer.
- An agent can have any number of sequences.
1. A sequence is written by extending the uvm_sequence
class mem_sequence extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item); `uvm_sequence_utils(mem_sequence,mem_sequencer) //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_sequence"); super.new(name); endfunction endclass
2. Logic to generate and send the sequence_item is added inside the body() method
class mem_sequence extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item); `uvm_sequence_utils(mem_sequence,mem_sequencer) //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_sequence"); super.new(name); endfunction virtual task body(); req = mem_seq_item::type_id::create("req"); wait_for_grant(); req.randomize(); send_request(req); wait_for_item_done(); endtask endclass write sequence
class mem_wr_seq extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item); `uvm_object_utils(mem_wr_seq) //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_wr_seq"); super.new(name); endfunction virtual task body(); `uvm_do_with(req,{req.wr_en == 1;}) endtask endclass read sequence
class mem_rd_seq extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item); `uvm_object_utils(mem_rd_seq) //Constructor function new(string name = "mem_rd_seq"); super.new(name); endfunction virtual task body(); `uvm_do_with(req,{req.rd_en == 1;}) endtask endclass Sequencer
Sequencer is written by extending uvm_sequencer, there is no extra logic required to be added in the sequencer.
class mem_sequencer extends uvm_sequencer#(mem_seq_item); `uvm_component_utils(mem_sequencer) //constructor function new(string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name,parent); endfunction endclass
Driver
driver receives the stimulus from sequence via sequencer and drives on interface signals.
1. driver is written by extending the uvm_driver
class mem_driver extends uvm_driver #(mem_seq_item); `uvm_component_utils(mem_driver) // Constructor function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new endclass : mem_driver
2. Declare the virtual interface,
// Virtual Interface virtual mem_if vif;
3. Get the interface handle using get config_db,
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual mem_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif)) `uvm_fatal("NO_VIF",{"virtual interface must be set for: ",get_full_name(),".vif"}); 4. adding the get config_db in the build_phase,
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); super.build_phase(phase); if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual mem_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif)) `uvm_fatal("NO_VIF",{"virtual interface must be set for: ",get_full_name(),".vif"}); endfunction: build_phase 5. Add driving logic. get the seq_item and drive to DUT signals,
// run phase virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); forever begin seq_item_port.get_next_item(req); ...... .. driving logic .. ...... seq_item_port.item_done(); end endtask : run_phase
Complete driver code,
class mem_driver extends uvm_driver #(mem_seq_item); // Virtual Interface virtual mem_if vif; `uvm_component_utils(mem_driver) //uvm_analysis_port #(mem_seq_item) Drvr2Sb_port; // Constructor function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); super.build_phase(phase); if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual mem_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif)) `uvm_fatal("NO_VIF",{"virtual interface must be set for: ",get_full_name(),".vif"}); endfunction: build_phase // run phase virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); forever begin seq_item_port.get_next_item(req); //respond_to_transfer(req); drive(); seq_item_port.item_done(); end endtask : run_phase // drive virtual task drive(); req.print(); `DRIV_IF.wr_en <= 0; `DRIV_IF.rd_en <= 0; @(posedge vif.DRIVER.clk); `DRIV_IF.addr <= req.addr; if(req.wr_en) begin `DRIV_IF.wr_en <= req.wr_en; `DRIV_IF.wdata <= req.wdata; //$display("\tADDR = %0h \tWDATA = %0h",req.addr,trans.wdata); @(posedge vif.DRIVER.clk); end if(req.rd_en) begin `DRIV_IF.rd_en <= req.rd_en; @(posedge vif.DRIVER.clk); `DRIV_IF.rd_en <= 0; @(posedge vif.DRIVER.clk); req.rdata = `DRIV_IF.rdata; // $display("\tADDR = %0h \tRDATA = %0h",trans.addr,`DRIV_IF.rdata); end $display("-----------------------------------------"); endtask : drive endclass : mem_driver Monitor
- Monitor samples the DUT signals through the virtual interface and converts the signal level activity to the transaction level.
1. The monitor is written by extending the uvm_monitor
class mem_monitor extends uvm_monitor; `uvm_component_utils(mem_monitor) // new - constructor function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new endclass : mem_monitor
2. Declare virtual interface,
// Virtual Interface virtual mem_if vif;
3. Connect interface to Virtual interface by using get method,
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); super.build_phase(phase); if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual mem_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif)) `uvm_fatal("NOVIF",{"virtual interface must be set for: ",get_full_name(),".vif"}); endfunction: build_phase 4. Declare analysis port,
uvm_analysis_port #(mem_seq_item) item_collected_port;
5. Declare seq_item handle, Used as a place holder for sampled signal activity,
mem_seq_item trans_collected;
6. Add Sampling logic in run_phase,
- sample the interface signal and assign to trans_collected handle
- sampling logic is placed in the forever loop
// run phase virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); forever begin //sampling logic @(posedge vif.MONITOR.clk); wait(vif.monitor_cb.wr_en || vif.monitor_cb.rd_en); trans_collected.addr = vif.monitor_cb.addr; if(vif.monitor_cb.wr_en) begin trans_collected.wr_en = vif.monitor_cb.wr_en; trans_collected.wdata = vif.monitor_cb.wdata; trans_collected.rd_en = 0; @(posedge vif.MONITOR.clk); end if(vif.monitor_cb.rd_en) begin trans_collected.rd_en = vif.monitor_cb.rd_en; trans_collected.wr_en = 0; @(posedge vif.MONITOR.clk); @(posedge vif.MONITOR.clk); trans_collected.rdata = vif.monitor_cb.rdata; end end endtask : run_phase
7. After sampling, by using the write method send the sampled transaction packet to the scoreboard,
item_collected_port.write(trans_collected);
Complete monitor code,
class mem_monitor extends uvm_monitor; // Virtual Interface virtual mem_if vif; uvm_analysis_port #(mem_seq_item) item_collected_port; // Placeholder to capture transaction information. mem_seq_item trans_collected; `uvm_component_utils(mem_monitor) // new - constructor function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); trans_collected = new(); item_collected_port = new("item_collected_port", this); endfunction : new function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); super.build_phase(phase); if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual mem_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif)) `uvm_fatal("NOVIF",{"virtual interface must be set for: ",get_full_name(),".vif"}); endfunction: build_phase // run phase virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); forever begin @(posedge vif.MONITOR.clk); wait(vif.monitor_cb.wr_en || vif.monitor_cb.rd_en); trans_collected.addr = vif.monitor_cb.addr; if(vif.monitor_cb.wr_en) begin trans_collected.wr_en = vif.monitor_cb.wr_en; trans_collected.wdata = vif.monitor_cb.wdata; trans_collected.rd_en = 0; @(posedge vif.MONITOR.clk); end if(vif.monitor_cb.rd_en) begin trans_collected.rd_en = vif.monitor_cb.rd_en; trans_collected.wr_en = 0; @(posedge vif.MONITOR.clk); @(posedge vif.MONITOR.clk); trans_collected.rdata = vif.monitor_cb.rdata; end item_collected_port.write(trans_collected); end endtask : run_phase endclass : mem_monitor Agent
An agent is a container class contains a driver, a sequencer, and a monitor.
1. agent is written by extending the uvm_agent,
class mem_agent extends uvm_agent; // UVM automation macros for general components `uvm_component_utils(mem_agent) // constructor function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new endclass : mem_agent
2. Declare driver, sequencer and monitor instance,
//declaring agent components mem_driver driver; mem_sequencer sequencer; mem_monitor monitor;
3. Depending on Agent type, create agent components in the build phase,
driver and sequencer will be created only for the active agent.
// build_phase function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); super.build_phase(phase); if(get_is_active() == UVM_ACTIVE) begin driver = mem_driver::type_id::create("driver", this); sequencer = mem_sequencer::type_id::create("sequencer", this); end monitor = mem_monitor::type_id::create("monitor", this); endfunction : build_phase 4. Connect the driver seq_item_port to sequencer seq_item_export for communication between driver and sequencer in the connect phase
// connect_phase function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase); if(get_is_active() == UVM_ACTIVE) begin driver.seq_item_port.connect(sequencer.seq_item_export); end endfunction : connect_phase
Complete Agent code,
class mem_agent extends uvm_agent; //declaring agent components mem_driver driver; mem_sequencer sequencer; mem_monitor monitor; // UVM automation macros for general components `uvm_component_utils(mem_agent) // constructor function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new // build_phase function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); super.build_phase(phase); if(get_is_active() == UVM_ACTIVE) begin driver = mem_driver::type_id::create("driver", this); sequencer = mem_sequencer::type_id::create("sequencer", this); end monitor = mem_monitor::type_id::create("monitor", this); endfunction : build_phase // connect_phase function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase); if(get_is_active() == UVM_ACTIVE) begin driver.seq_item_port.connect(sequencer.seq_item_export); end endfunction : connect_phase endclass : mem_agent Scoreboard
scoreboard receives the transaction from the monitor and compares it with the reference values.
1. The scoreboard is written by extending uvm_scoreboard,
class mem_scoreboard extends uvm_scoreboard; `uvm_component_utils(mem_scoreboard) // new - constructor function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new endclass : mem_scoreboard
2. Declare and Create TLM Analysis port, ( to receive transaction pkt from Monitor),
//Declaring port uvm_analysis_imp#(mem_seq_item, mem_scoreboard) item_collected_export; //creating port item_collected_export = new("item_collected_export", this); 3. The analysis export of Scoreboard is connected to the Monitor port. (Connection is done in environment connect phase)
monitor.item_collected_port.connect(scoreboard.item_collected_export);
4. write method of the scoreboard will receive the transaction packet from the monitor, on calling write method from the monitor
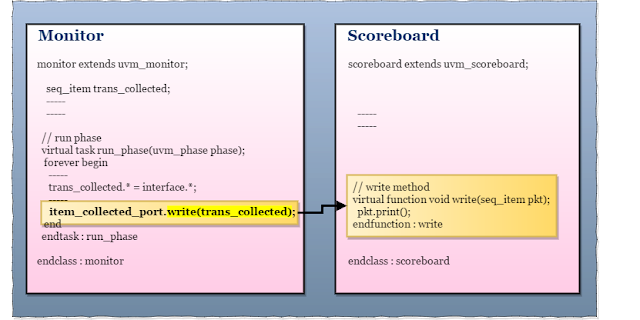
//calling write method from monitor item_collected_port.write(pkt); //scoreboard write function virtual function void write(mem_seq_item pkt); pkt.print(); endfunction : write
6. Add Sampling logic in run_phase,
// run phase virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); --- comparision logic --- endtask : run_phase
Complete scoreboard code
class mem_scoreboard extends uvm_scoreboard; `uvm_component_utils(mem_scoreboard) uvm_analysis_imp#(mem_seq_item, mem_scoreboard) item_collected_export; // new - constructor function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); super.build_phase(phase); item_collected_export = new("item_collected_export", this); endfunction: build_phase // write virtual function void write(mem_seq_item pkt); $display("SCB:: Pkt recived"); pkt.print(); endfunction : write // run phase virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); --- comparision logic --- endtask : run_phase endclass : mem_scoreboard Environment/env
The environment is the container class, It contains one or more agents, as well as other components such as the scoreboard, top-level monitor, and checker.
1. The environment is written by extending the uvm_env,
class mem_model_env extends uvm_env; `uvm_component_utils(mem_model_env) // new - constructor function new(string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new endclass : mem_model_env
2. Declare the agent and scoreboard,
mem_agent mem_agnt; mem_scoreboard mem_scb;
3. Create agent and scoreboard,
mem_agnt = mem_agent::type_id::create("mem_agnt", this); mem_scb = mem_scoreboard::type_id::create("mem_scb", this); 3. Connecting monitor port to scoreboard port,
mem_agnt.monitor.item_collected_port.connect(mem_scb.item_collected_export);
Complete environment code,
class mem_model_env extends uvm_env; //--------------------------------------- // agent and scoreboard instance //--------------------------------------- mem_agent mem_agnt; mem_scoreboard mem_scb; `uvm_component_utils(mem_model_env) //--------------------------------------- // constructor //--------------------------------------- function new(string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new //--------------------------------------- // build_phase - crate the components //--------------------------------------- function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); super.build_phase(phase); mem_agnt = mem_agent::type_id::create("mem_agnt", this); mem_scb = mem_scoreboard::type_id::create("mem_scb", this); endfunction : build_phase //--------------------------------------- // connect_phase - connecting monitor and scoreboard port //--------------------------------------- function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase); mem_agnt.monitor.item_collected_port.connect(mem_scb.item_collected_export); endfunction : connect_phase endclass : mem_model_env Test
The test defines the test scenario for the testbench.
1. test is written by extending the uvm_test,
class mem_model_test extends uvm_test; `uvm_component_utils(mem_model_test) function new(string name = "mem_model_test",uvm_component parent=null); super.new(name,parent); endfunction : new endclass : mem_model_test
2. Declare env and sequence,
mem_model_env env; mem_sequence seq;
3. Create env and sequence,
env = mem_model_env::type_id::create("env",this); seq = mem_sequence::type_id::create("seq"); 4. Start sequence,
seq.start(env.mem_agnt.sequencer);
Complete Test code,
class mem_model_test extends uvm_test; `uvm_component_utils(mem_model_test) mem_model_env env; mem_sequence seq; function new(string name = "mem_model_test",uvm_component parent=null); super.new(name,parent); endfunction : new virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); super.build_phase(phase); env = mem_model_env::type_id::create("env", this); seq = mem_sequence::type_id::create("seq"); endfunction : build_phase task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); phase.raise_objection(this); seq.start(env.mem_agnt.sequencer); phase.drop_objection(this); endtask : run_phase endclass : mem_model_test TestBench_Top
TestBench top is the module, it connects the DUT and Verification environment components.
Testbench_top contains,
- DUT instance
- interface instance
- run_test() method
- virtual interface set config_db
- clock and reset generation logic
- wave dump logic
run test
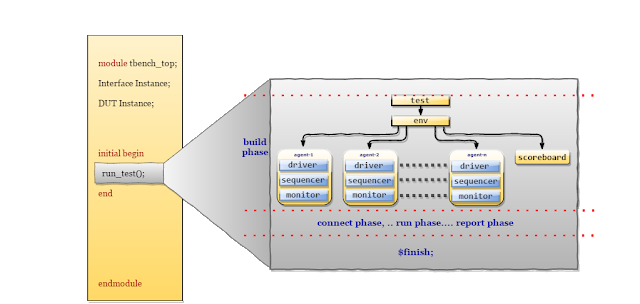
module tbench_top; //clock and reset signal declaration bit clk; bit reset; //clock generation always #5 clk = ~clk; //reset Generation initial begin reset = 1; #5 reset =0; end //creatinng instance of interface, inorder to connect DUT and testcase mem_if intf(clk,reset); //DUT instance, interface signals are connected to the DUT ports memory DUT ( .clk(intf.clk), .reset(intf.reset), .addr(intf.addr), .wr_en(intf.wr_en), .rd_en(intf.rd_en), .wdata(intf.wdata), .rdata(intf.rdata) ); //enabling the wave dump initial begin uvm_config_db#(virtual mem_if)::set(uvm_root::get(),"*","vif",intf); $dumpfile("dump.vcd"); $dumpvars; end initial begin run_test(); end endmodule Edit and Execute the Memory Model UVM TestBench code in EDA Playground.
