Options (9)
Scale (2)
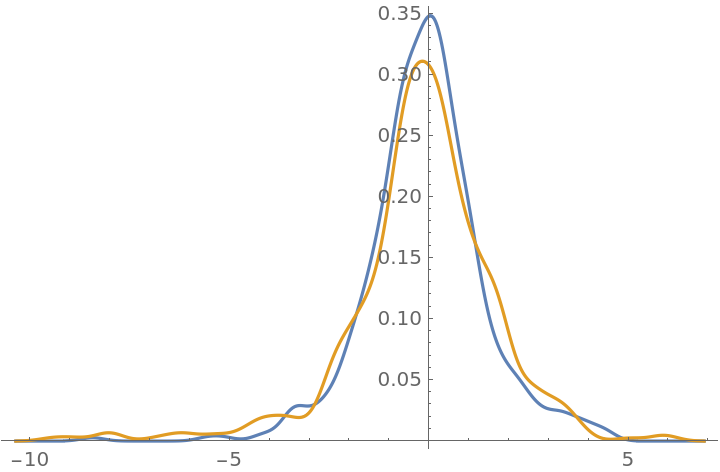
If f has multiple peaks, the algorithm can get stuck in the one nearest to the starting point:
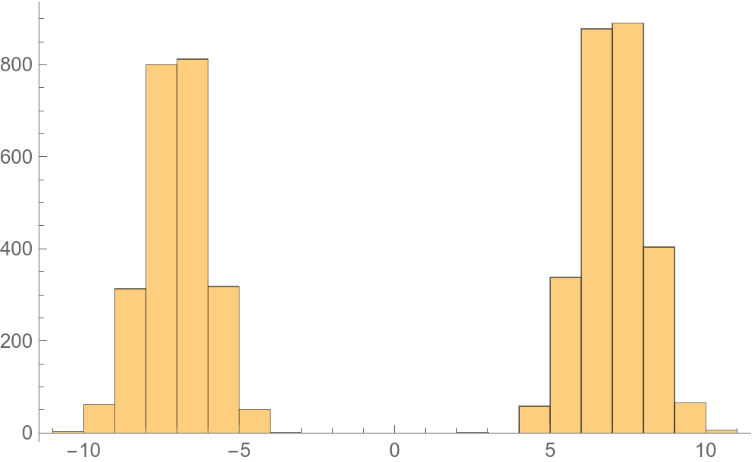
Use a larger "Scale" to explore the whole landscape:
JumpDistribution (2)
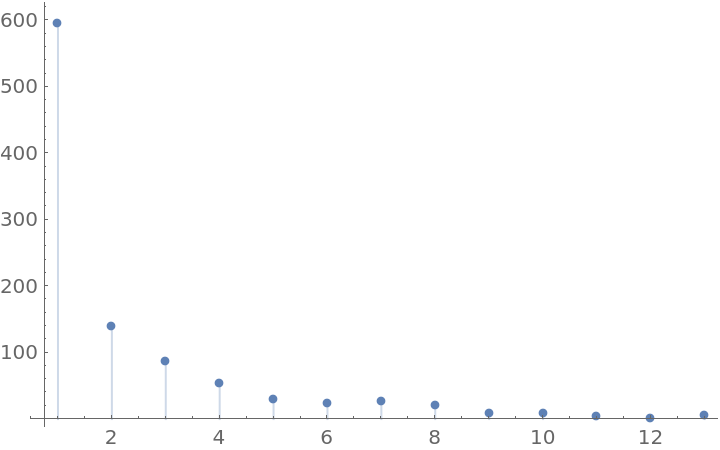
Use a discrete jump distribution to approximate discrete distributions:
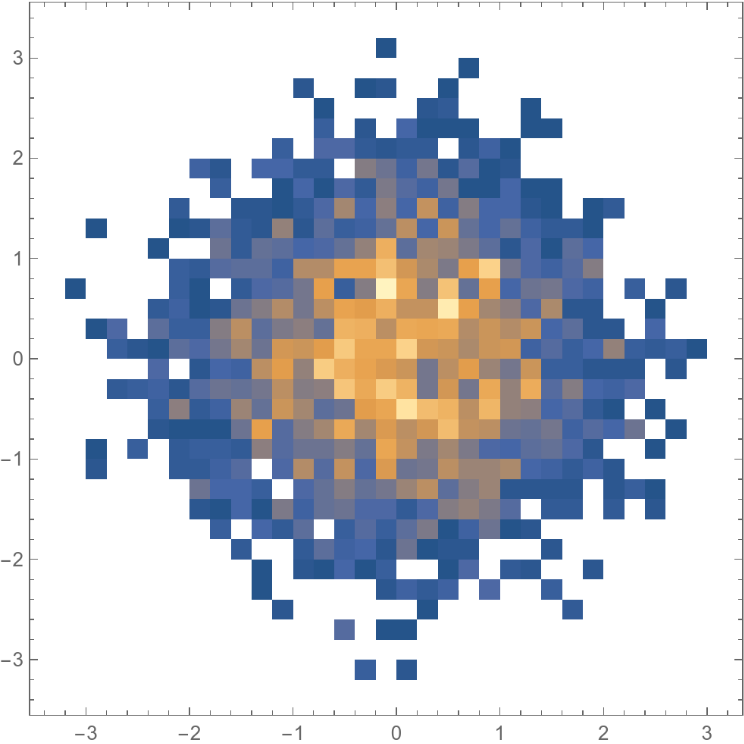
Multivariate example:
WorkingPrecision (1)
Use WorkingPrecision to get higher precision in parameter estimates:
ShowRejectionRate (2)
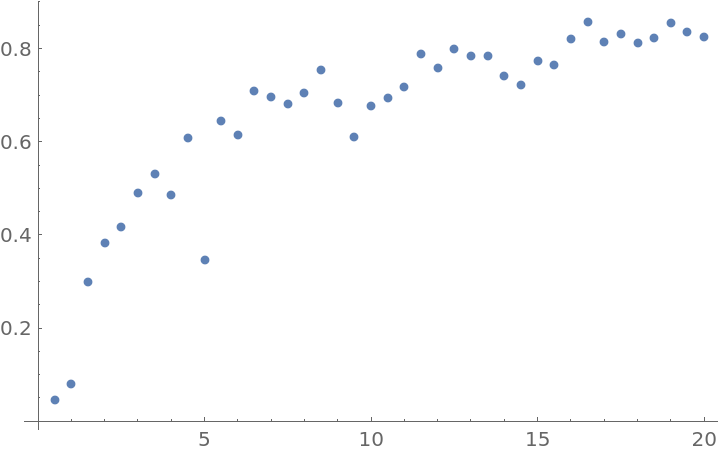
Use "ShowRejectionRate" to see the rejection rate of the process:
"ShowRejectionRate" can be used to select an optimal "Scale" for the method ("RejectionRate" is usually advised to be between 50% and 80% [see References]):
LogProbability (1)
Use "LogProbability" to generate samples from a distribution defined by the Log of its PDF:
Applications (4)
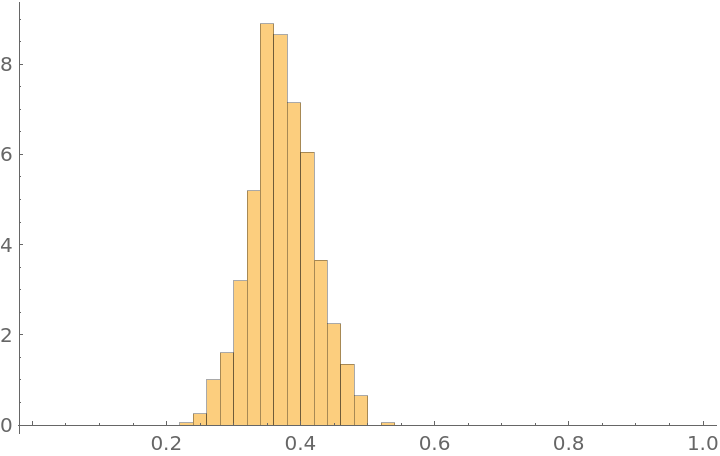
Generate sample data using BernoulliDistribution:
Define a prior distribution for the parameter (in this case, the Jeffreys prior):
Use Bayes's rule and multiply the Likelihood with the prior to get an f function, which is proportional to the posterior distribution of the parameter:
Use MetropolisHastingsSequence to generate one thousand samples of the θ parameter and create a Histogram:
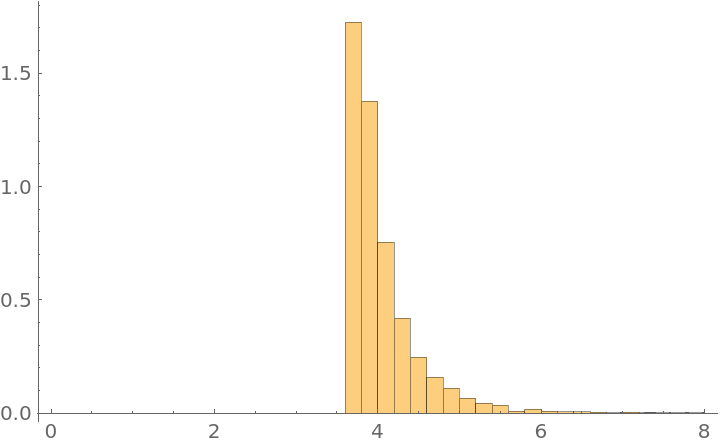
Infer the parameter of a UniformDistribution (also know as the German tank problem). First, generate a small sample of data using UniformDistribution:
Define a prior distribution for the parameter (in this case, the non-normalizable Jeffreys prior):
Use Bayes's rule and multiply the Likelihood with the prior to get a function that is proportional to the posterior distribution of the parameter:
Use MetropolisHastingsSequence to generate one thousand samples of the θ parameter and generate a Histogram:
Generate sample data using NormalDistribution:
Define a prior distribution for the parameter (in this case, the scale-free non-normalizable prior):
Use Bayes's rule and multiply the Likelihood with the prior to get a function that is proportional to the posterior distribution of the parameter:
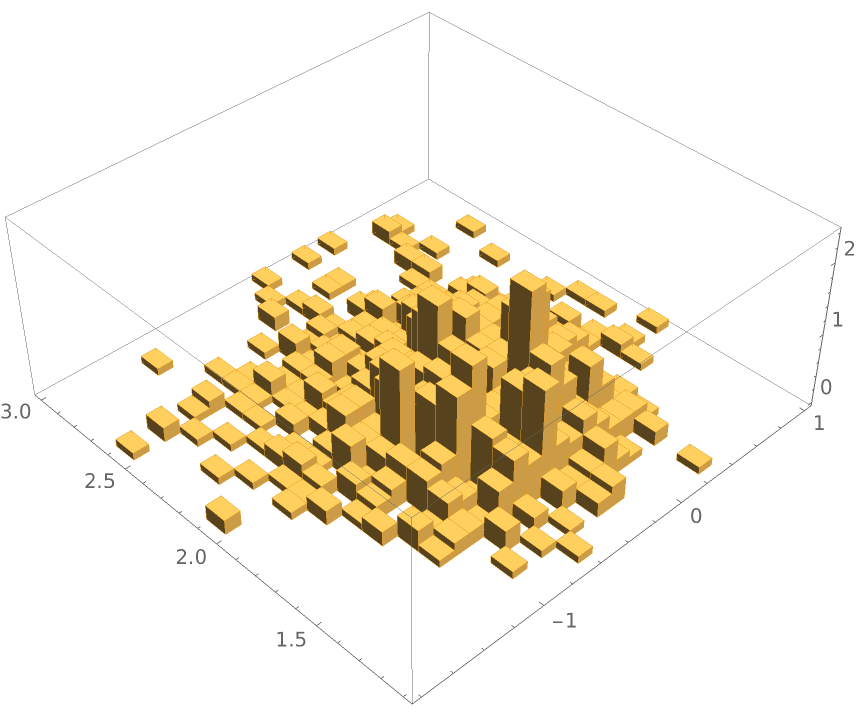
Use MetropolisHastingsSequence to generate one thousand samples of the {μ,σ} pair of parameters and generate a Histogram3D:
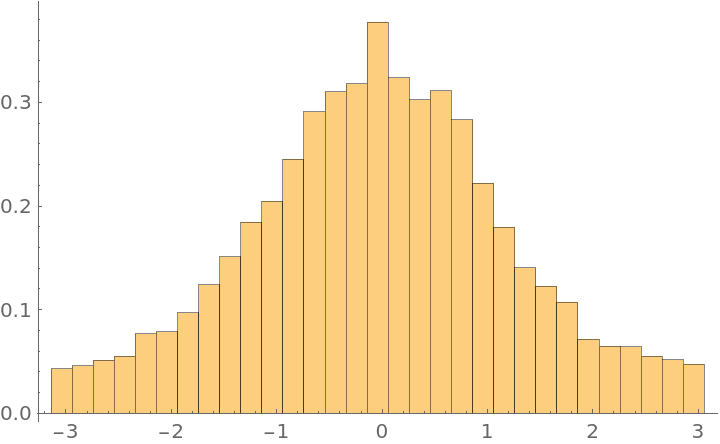
Generating a sample from distribution with PDF  defined on a circle:
defined on a circle:
Possible Issues (2)
The parameter thin should be an integer greater than 0:
The dimension of the parameter-dependent "JumpDistribution" must match the number of variables:
![(SeedRandom[1234]; ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][E^(-x^2/ 2), {x, 0}, {100, 100, 10}, Method -> Automatic]) == (SeedRandom[ 1234]; ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][E^(-x^2/ 2), {x, 0}, {100, 100, 10}, Method -> "CustomSymmetricJump", "JumpDistribution" -> (NormalDistribution[#, 1] &)])](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/189/189a6b3c-6587-45e1-b843-d946422b03d1/6934f8f82085ee1b.png)
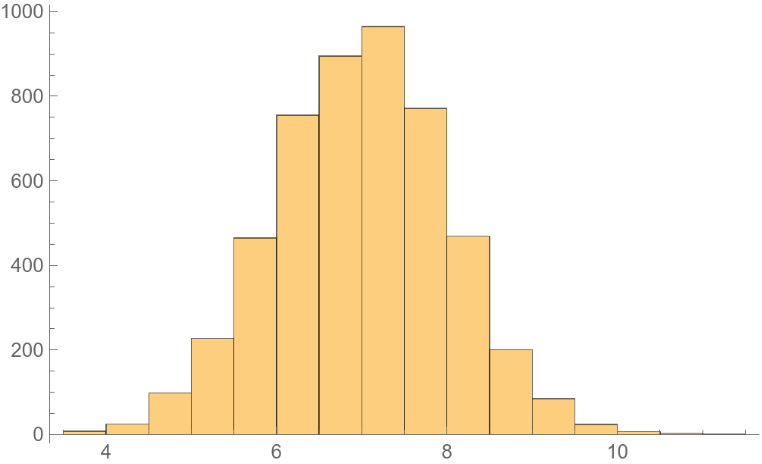
![ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][ E^(-(x - 7)^2/2) + E^(-(x + 7)^2/2), {x, 1}, {5000, 100, 10}, "Scale" -> 5] // Histogram](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/189/189a6b3c-6587-45e1-b843-d946422b03d1/2da141ce9b066074.png)
![ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][ E^(-((x^2 + y^2)/2)), {{x, 0}, {y, 0}}, {5000, 100, 1}, Method -> "CustomSymmetricJump", "JumpDistribution" -> (MultivariateTDistribution[#, IdentityMatrix[2], 3] &)] // DensityHistogram](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/189/189a6b3c-6587-45e1-b843-d946422b03d1/71d5a3baa1cff051.png)


![Table[{\[Sigma], "RejectionRate" /. Last[ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][ 1/(1 + x^2), {x, 0}, {100, 0, 10}, "ShowRejectionRate" -> True, "Scale" -> \[Sigma]]]}, {\[Sigma], 0.5, 20, 0.5}] // ListPlot](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/189/189a6b3c-6587-45e1-b843-d946422b03d1/79d20828cafab3a8.png)
![Histogram[ ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][ f, {\[Theta], 1/2}, {1000, 100, 10}], {0, 1, Automatic}, "ProbabilityDensity"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/189/189a6b3c-6587-45e1-b843-d946422b03d1/3ca3c660dc6bd439.png)
![Histogram[ ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][ f, {\[Theta], 8}, {5000, 100, 10}], {0, 8, Automatic}, "ProbabilityDensity"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/189/189a6b3c-6587-45e1-b843-d946422b03d1/13a6cb6471760638.png)
![Quiet[Histogram3D[ ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][ f, {{\[Mu], 0}, {\[Sigma], 1}}, {1000, 100, 10}], {Automatic, {0, 3, Automatic}}, "ProbabilityDensity"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/189/189a6b3c-6587-45e1-b843-d946422b03d1/75b3ce8bf590ce5d.png)
![]() defined on a circle:
defined on a circle:![Histogram[ Mod[ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][ E^-(1 - Cos[\[CurlyPhi]]), {\[CurlyPhi], 0}, {10000, 100, 10}], 2 \[Pi], -\[Pi]], {-\[Pi], \[Pi], Automatic}, "ProbabilityDensity"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/189/189a6b3c-6587-45e1-b843-d946422b03d1/19e0cd10f285b015.png)
![\[ScriptCapitalD] = ProbabilityDistribution[ 1/\[Pi] 1/Cosh[x], {x, -\[Infinity], \[Infinity]}]; data1 = RandomVariate[\[ScriptCapitalD], 500]; data2 = ResourceFunction["MetropolisHastingsSequence"][ 1/Cosh[x], {x, 0}, {500, 100, 10}]; KolmogorovSmirnovTest[data1, data2]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/189/189a6b3c-6587-45e1-b843-d946422b03d1/063c76579667681d.png)