Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Restructure an expression with nested AmbiguityList expressions into a single flat AmbiguityList
ResourceFunction["FlattenAmbiguityList"][expr] restructures expr as a single AmbiguityList. | |
ResourceFunction["FlattenAmbiguityList"][expr, n] limits to no more than n possibilities. | |
ResourceFunction["FlattenAmbiguityList"][expr, n, crit] limits to no more than n possibilities pi for which crit[pi] is True. |
AmbiguityList is often only wrapped around the ambiguous part of an expression:
| In[1]:= | |
| Out[1]= | |
By moving the arguments inside the listed functions, all possible values can be computed directly:
| In[2]:= | |
| Out[2]= | |
Interpreter can return nested AmbiguityList expressions that may be difficult to reason about:
| In[3]:= | |
| Out[3]= | 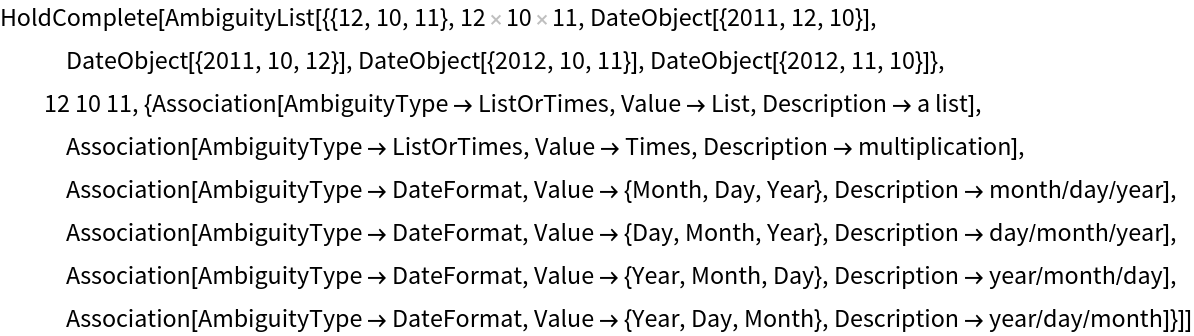 |
Flatten the expression to see all possibilities in a single flat list:
| In[4]:= | |
| Out[4]= | 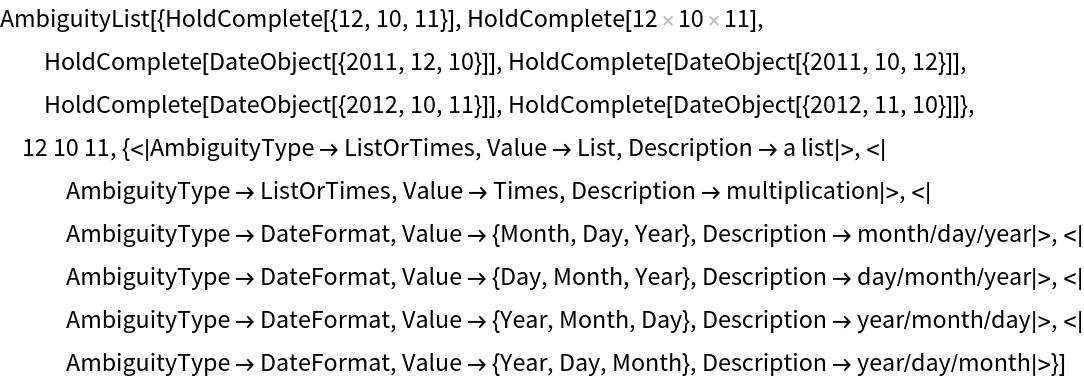 |
Ambiguous expressions can produce a large number of possibilities:
| In[5]:= | |
| Out[5]= |  |
| In[6]:= | |
| Out[6]= | |
Limit the number of distinct possibilities produced:
| In[7]:= | |
| Out[7]= | 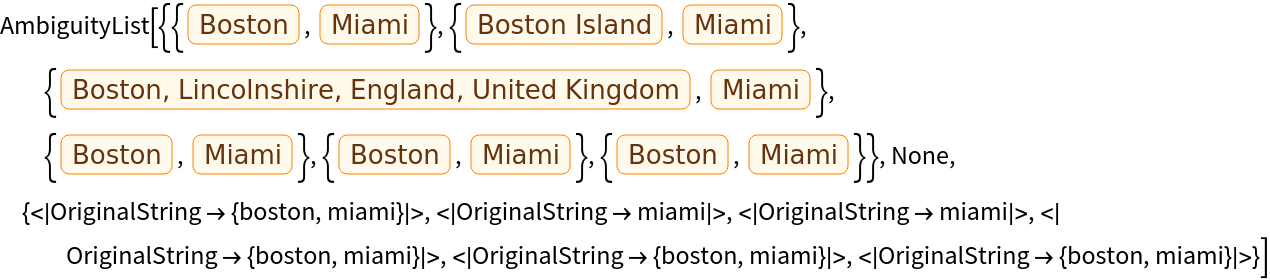 |
Also limit to possibilities that pass a selection function:
| In[8]:= | |
| Out[8]= | 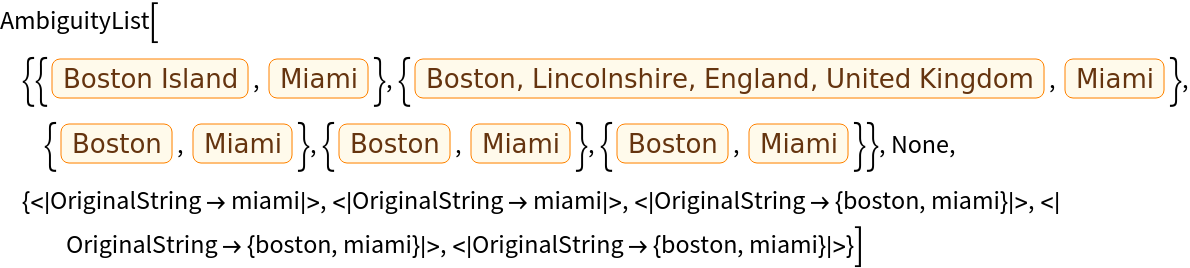 |
By default, only preexisting metadata is maintained during restructuring:
| In[9]:= | ![congo = ResourceFunction["FlattenAmbiguityList"][ AmbiguityList[{Entity["Country", "DemocraticRepublicCongo"], Entity["Country", "RepublicCongo"], Entity["Language", "KongoSanSalvador::9rdzh"], Entity["Language", "Koongo::9wqpj"], Entity["River", "Congo::zqkh9"], Entity["Movie", "Congo::mf7gc"], Entity["Word", "congo"]}] ]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4f0/4f0164b5-bdbf-46af-b1de-3ab6d63b4ab1/438cc2cac3284166.png) |
| Out[9]= |  |
Add an entity type to descriptions for further clarity:
| In[10]:= | |
| Out[10]= |  |
Show metadata alongside possibilities:
| In[11]:= | |
| Out[11]= | 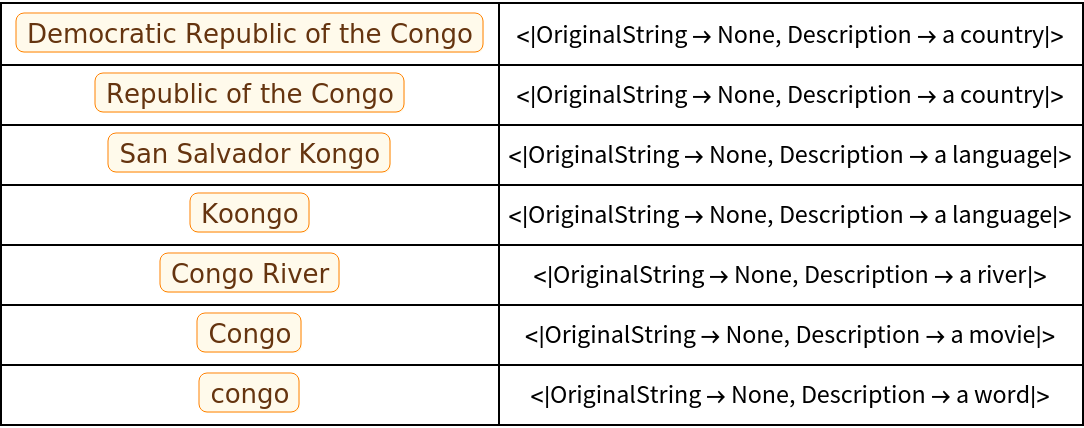 |
Find all interpretations for a food using an ambiguous unit of "cup":
| In[12]:= | |
| Out[12]= |  |
Flatten the expression to see each interpretation:
| In[13]:= | |
| Out[13]= |  |
Compare calorie amounts for different interpretations of the unit:
| In[14]:= | |
| Out[14]= | 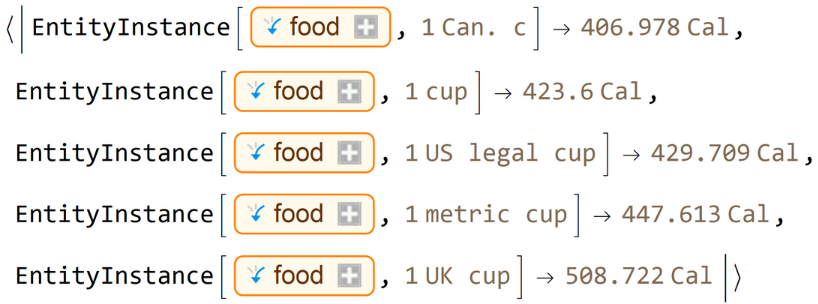 |
Unambiguous expressions are not restructured:
| In[15]:= | |
| Out[15]= | |
An already-flat AmbiguityList is not restructured:
| In[16]:= | ![ResourceFunction["FlattenAmbiguityList"][#] === # &[ AmbiguityList[{Entity["Country", "DemocraticRepublicCongo"], Entity["Country", "RepublicCongo"], Entity["River", "Congo::zqkh9"], Entity["Movie", "Congo::mf7gc"], Entity["Language", "KongoSanSalvador::9rdzh"], Entity["Language", "Koongo::9wqpj"], Entity["Word", "congo"]}]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4f0/4f0164b5-bdbf-46af-b1de-3ab6d63b4ab1/205f146938181df3.png) |
| Out[16]= | |
Expressions containing AmbiguityList in deeper parts of an expression will be moved to the top level:
| In[17]:= | ![ResourceFunction[ "FlattenAmbiguityList"][{123, AmbiguityList[{Entity[ "City", {"Springfield", "Illinois", "UnitedStates"}], Entity["City", {"Springfield", "Missouri", "UnitedStates"}]}, "springfield"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4f0/4f0164b5-bdbf-46af-b1de-3ab6d63b4ab1/3b69b0db37a87bf9.png) |
| Out[17]= | |
If ambiguity is present, a selection function that produces no matches returns an empty AmbiguityList:
| In[18]:= | ![ResourceFunction["FlattenAmbiguityList"][ AmbiguityList[{{AmbiguityList[{"a1", "a2", "a3"}, "A"], AmbiguityList[{"b1", "b2", "b3"}, "B"]}}], All, FreeQ[_String]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4f0/4f0164b5-bdbf-46af-b1de-3ab6d63b4ab1/564e5e7964a5369d.png) |
| Out[18]= | |
When no ambiguity is present, the expression is left untouched:
| In[19]:= | |
| Out[19]= | |
Sometimes ambiguous expressions can produce a large number of possibilities, which can take excessive memory and computation time:
| In[20]:= | ![MemoryConstrained[ Length@First@ ResourceFunction["FlattenAmbiguityList"][ SemanticInterpretation["springfield, boston", AmbiguityFunction -> All]], 100*10^6 ]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4f0/4f0164b5-bdbf-46af-b1de-3ab6d63b4ab1/1f1fb6720bd14244.png) |
| Out[21]= | |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License