Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2293. Min Max Game
Description
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums whose length is a power of 2.
Apply the following algorithm on nums:
- Let
nbe the length ofnums. Ifn == 1, end the process. Otherwise, create a new 0-indexed integer arraynewNumsof lengthn / 2. - For every even index
iwhere0 <= i < n / 2, assign the value ofnewNums[i]asmin(nums[2 * i], nums[2 * i + 1]). - For every odd index
iwhere0 <= i < n / 2, assign the value ofnewNums[i]asmax(nums[2 * i], nums[2 * i + 1]). - Replace the array
numswithnewNums. - Repeat the entire process starting from step 1.
Return the last number that remains in nums after applying the algorithm.
Example 1:
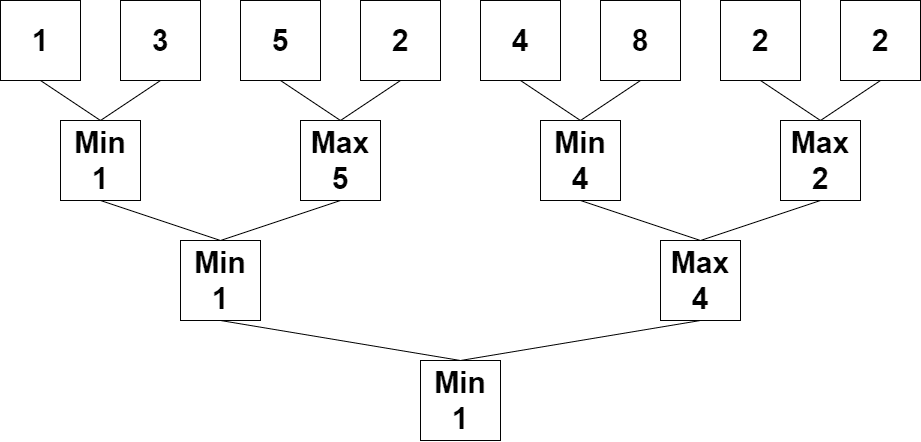
Input: nums = [1,3,5,2,4,8,2,2] Output: 1 Explanation: The following arrays are the results of applying the algorithm repeatedly. First: nums = [1,5,4,2] Second: nums = [1,4] Third: nums = [1] 1 is the last remaining number, so we return 1.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3] Output: 3 Explanation: 3 is already the last remaining number, so we return 3.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10241 <= nums[i] <= 109nums.lengthis a power of2.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int minMaxGame(int[] nums) { for (int n = nums.length; n > 1;) { n >>= 1; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int a = nums[i << 1], b = nums[i << 1 | 1]; nums[i] = i % 2 == 0 ? Math.min(a, b) : Math.max(a, b); } } return nums[0]; } } -
class Solution { public: int minMaxGame(vector<int>& nums) { for (int n = nums.size(); n > 1;) { n >>= 1; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int a = nums[i << 1], b = nums[i << 1 | 1]; nums[i] = i % 2 == 0 ? min(a, b) : max(a, b); } } return nums[0]; } }; -
class Solution: def minMaxGame(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: n = len(nums) while n > 1: n >>= 1 for i in range(n): a, b = nums[i << 1], nums[i << 1 | 1] nums[i] = min(a, b) if i % 2 == 0 else max(a, b) return nums[0] -
func minMaxGame(nums []int) int { for n := len(nums); n > 1; { n >>= 1 for i := 0; i < n; i++ { a, b := nums[i<<1], nums[i<<1|1] if i%2 == 0 { nums[i] = min(a, b) } else { nums[i] = max(a, b) } } } return nums[0] } -
function minMaxGame(nums: number[]): number { for (let n = nums.length; n > 1; ) { n >>= 1; for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { const a = nums[i << 1]; const b = nums[(i << 1) | 1]; nums[i] = i % 2 == 0 ? Math.min(a, b) : Math.max(a, b); } } return nums[0]; } -
impl Solution { pub fn min_max_game(mut nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 { let mut n = nums.len(); while n != 1 { n >>= 1; for i in 0..n { nums[i] = (if (i & 1) == 1 { i32::max } else { i32::min })( nums[i << 1], nums[(i << 1) | 1] ); } } nums[0] } }