Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1740. Find Distance in a Binary Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary tree and two integers p and q, return the distance between the nodes of value p and value q in the tree.
The distance between two nodes is the number of edges on the path from one to the other.
Example 1:
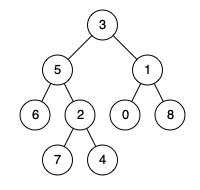
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 0 Output: 3 Explanation: There are 3 edges between 5 and 0: 5-3-1-0.
Example 2:

Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 7 Output: 2 Explanation: There are 2 edges between 5 and 7: 5-2-7.
Example 3:

Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 5 Output: 0 Explanation: The distance between a node and itself is 0.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 109- All
Node.valare unique. pandqare values in the tree.
Solutions
Related: 236-Lowest-Common-Ancestor-of-a-Binary-Tree/
First, find the lowest common ancestor of the two nodes with values p and q. Next, calculate the distances from the lowest common ancestor to the two nodes with values p and q, respectively. Finally, calculate the sum of the two distances and return.
Alternative-1
hashmap to store distance of every node-pair during finding LCA, then just map look up.
Alternative-2
Dist(n1, n2) = Dist(root, n1) + Dist(root, n2) - 2 * Dist(root, lca)
- ‘n1’ and ‘n2’ are the two given keys
- ‘root’ is root of given Binary Tree.
- ‘lca’ is lowest common ancestor of n1 and n2
- Dist(n1, n2) is the distance between n1 and n2.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public int findDistance(TreeNode root, int p, int q) { TreeNode g = lca(root, p, q); return dfs(g, p) + dfs(g, q); } private int dfs(TreeNode root, int v) { if (root == null) { return -1; } if (root.val == v) { return 0; } int left = dfs(root.left, v); int right = dfs(root.right, v); if (left == -1 && right == -1) { return -1; } return 1 + Math.max(left, right); } private TreeNode lca(TreeNode root, int p, int q) { if (root == null || root.val == p || root.val == q) { return root; } TreeNode left = lca(root.left, p, q); TreeNode right = lca(root.right, p, q); if (left == null) { return right; } if (right == null) { return left; } return root; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int findDistance(TreeNode* root, int p, int q) { TreeNode* g = lca(root, p, q); return dfs(g, p) + dfs(g, q); } TreeNode* lca(TreeNode* root, int p, int q) { if (!root || root->val == p || root->val == q) return root; TreeNode* left = lca(root->left, p, q); TreeNode* right = lca(root->right, p, q); if (!left) return right; if (!right) return left; return root; } int dfs(TreeNode* root, int v) { if (!root) return -1; if (root->val == v) return 0; int left = dfs(root->left, v); int right = dfs(root->right, v); if (left == -1 && right == -1) return -1; return 1 + max(left, right); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def findDistance(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], p: int, q: int) -> int: def lca(root, p, q): if root is None or root.val in [p, q]: return root left = lca(root.left, p, q) right = lca(root.right, p, q) if left is None: return right if right is None: return left return root def dfs(root, v): if root is None: return -1 if root.val == v: return 0 left, right = dfs(root.left, v), dfs(root.right, v) if left == right == -1: return -1 return 1 + max(left, right) g = lca(root, p, q) return dfs(g, p) + dfs(g, q) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func findDistance(root *TreeNode, p int, q int) int { var lca func(root *TreeNode, p int, q int) *TreeNode lca = func(root *TreeNode, p int, q int) *TreeNode { if root == nil || root.Val == p || root.Val == q { return root } left, right := lca(root.Left, p, q), lca(root.Right, p, q) if left == nil { return right } if right == nil { return left } return root } var dfs func(root *TreeNode, v int) int dfs = func(root *TreeNode, v int) int { if root == nil { return -1 } if root.Val == v { return 0 } left, right := dfs(root.Left, v), dfs(root.Right, v) if left == -1 && right == -1 { return -1 } return 1 + max(left, right) } g := lca(root, p, q) return dfs(g, p) + dfs(g, q) }