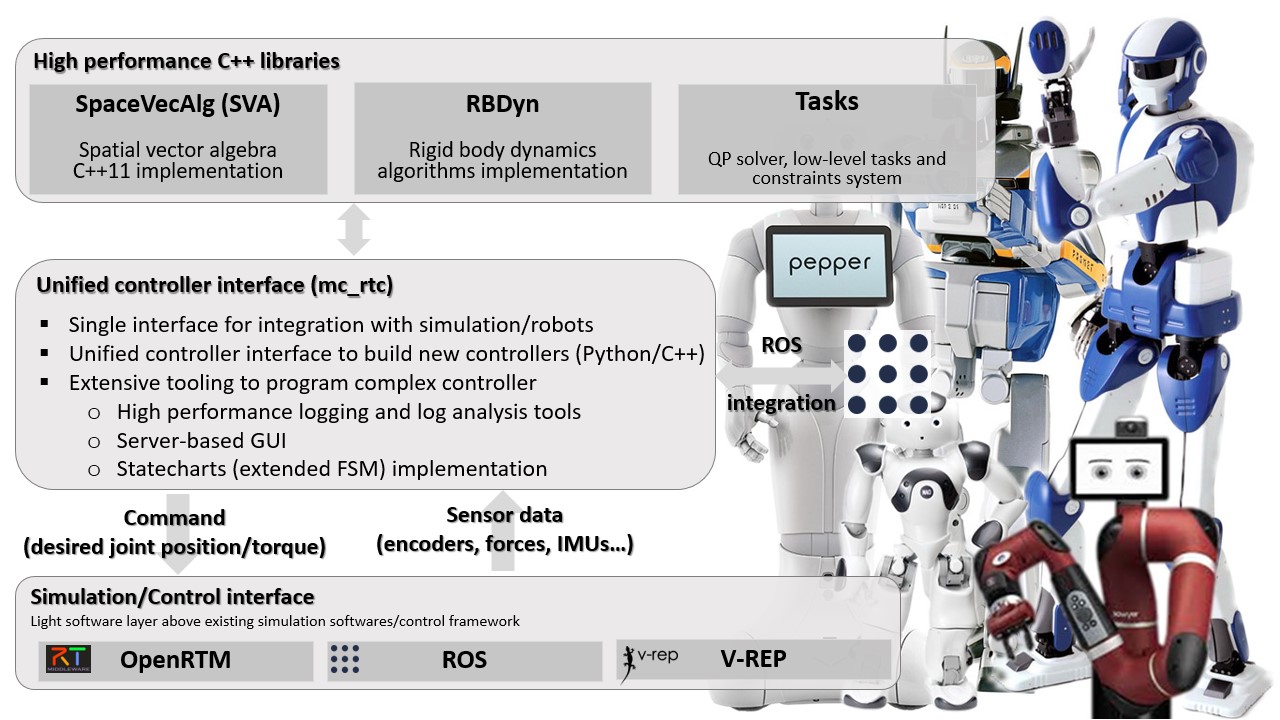
mc_rtc::Configuration general purpose configurationmc_rtc is an interface for simulation and robot control systems. These systems should provide the state of a given robot (joints’ values, sensor readings…) and in return mc_rtc will provide the desired robot’s state (command). This is done through the mc_control::MCGlobalController class. This class does not perform control by itself but rather delegates this task to the mc_control::MCController derived objects that it holds. Writing a controller within the mc_rtc framework is done by writing a class that inherits from the mc_control::MCController base class and implements the required functionnality. We implement such a controller in the following tutorials. The present tutorial simply explains how to build/install the framework on your machine.
We provide binaries for the current Ubuntu LTS releases and macOS via Homebrew. We also provide a source release using an easy-to-use script for Ubuntu, macOS and Windows and a vcpkg registry.
Binaries are recommended for Ubuntu users and macOS users. vcpkg is recommended for Windows users.
# Setup the mirror curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/mc-rtc/stable/setup.deb.sh' | sudo -E bash # Install packages sudo apt install libmc-rtc-dev mc-rtc-utils # Assuming you have a ROS distribution mirror setup sudo apt install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-mc-rtc-plugin ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-mc-rtc-tools# Setup the mirror curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/mc-rtc/head/setup.deb.sh' | sudo -E bash # Install packages sudo apt install libmc-rtc-dev mc-rtc-utils # Assuming you have a ROS distribution mirror setup sudo apt install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-mc-rtc-plugin ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-mc-rtc-toolsNote: the distributed version of mc_rtc runs with the QLD QP solver through eigen-qld. If you have access to the LSSOL solver and thus can install eigen-lssol then you can build Tasks with LSSOL support and install it in /usr. The two versions are binary compatible.
Follow the official instructions to install Homebrew. Then:
brew tap mc-rtc/mc-rtc brew install mc_rtcFollow vcpkg instruction to install vcpkg on your system.
You can then setup our registry by creating a vcpkg-configuration.json file either alongside the vcpkg binary or alongside your vcpkg.json manifest:
{ "registries": [ { "kind": "git", "baseline": "{see below}", "repository": "https://github.com/mc-rtc/vcpkg-registry", "packages": [ "libnotify", "hpp-spline", "ndcurves", "tvm", "spacevecalg", "rbdyn", "eigen-qld", "sch-core", "tasks", "mc-rbdyn-urdf", "mc-rtc-data", "eigen-quadprog", "state-observation", "mc-rtc" ] } ] }Where baseline should be the latest commit sha1 on mc-rtc/vcpkg-registry
You can then either:
vcpkg command: vcpkg install mc_rtcvcpkg.json file), such as the following example:{ "name": "my-package", "version-string": "1.0.0", "homepage": "https://my.home", "description": "My package description", "dependencies": [ "mc-rtc" ] }mc-rtc-superbuild is a CMake-based option to build mc_rtc and its dependencies. It also provides an extension mechanism to that you can build projects that require mc_rtc.
Please refer to the project’s homepage for usage instructions.
The following options are also available but are deprecated:
Once mc_rtc has been installed, you can jump to the next section.