8751. Getting Started with ExpressExpress
Introduce how to setup web server with express in Node.js.
1. What is Express?
Express is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications. It is the standard web server framework for Node.js. Some notes of this posting comes from the book - Express in Action.
1.1 Hello World
A standard way to setup web server with express.
// helloworld.js // Requires Express and puts it in a variable var express = require("express"); // Calls express() and puts new Express application inside the app variable var app = express(); // Sends “Hello, world!” app.get("/", function(request, response) { response.send("Hello, world!"); }); //Starts the Express server on port 3000 and logs that it has started app.listen(3000, function() { console.log("Express app started on port 3000."); }); 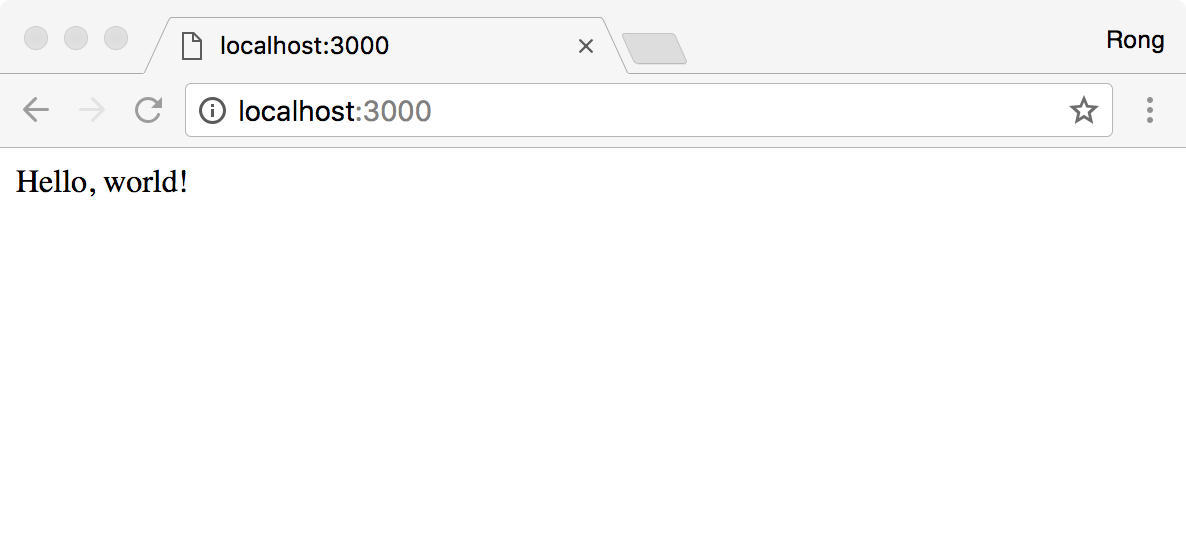
2. Express Core
Express has four major features:
Middleware: An array of functions to process incoming requests.Routing: Rules how an application’s endpoints (URIs) respond to client requests.Extensions: Extends the request and response objects with extra methods and properties.Views: Dynamically render HTML at server side.
3. Web Server
3.1 Node Http Module
Actually, we can create web server with node http module without using express.
// httpserver.js var http = require("http"); function requestHandler(request, response) { console.log("In comes a request to: " + request.url); response.end("Hello, world(http)!"); } var server = http.createServer(requestHandler); server.listen(3000, function() { console.log("Web server(http) started on port 3000."); }); 3.2 Http + Express
// httpexpress.js var express = require("express"); var http = require("http"); var app = express(); app.use(function(request, response) { console.log("In comes a request to: " + request.url); response.end("Hello, world(http+express)!"); }); http.createServer(app).listen(3000, function() { console.log("Web server(http+express) started on port 3000."); }); 3.3 Express Only
// expressserver.js var express = require("express"); var app = express(); app.use(function(request, response) { console.log("In comes a request to: " + request.url); response.end("Hello, world(express)!"); }); app.listen(3000, function() { console.log("Web server(express) started on port 3000."); }); 4. Other Usage
1) Enable CORS
app.use(function(req, res, next) { res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*"); res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept"); res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "*"); next(); }); 2) Query arguments, /search?q=javascript
app.get("/search", function(req, res) { req.query.q == "best restaurant" // ... }); 3) Redirect
response.redirect("/hello/world"); response.redirect("http://expressjs.com"); 4) Https
// https var express = require("express"); var https = require("https"); var fs = require("fs"); var app = express(); // ... define your app ... var httpsOptions = { key: fs.readFileSync("path/to/private/key.pem"), cert: fs.readFileSync("path/to/certificate.pem") }; https.createServer(httpsOptions, app).listen(3000); 5) Run both an HTTP server and an HTTPS server.
var express = require("express"); var http = require("http"); var https = require("https"); var fs = require("fs"); var app = express(); // ... define your app ... var httpsOptions = { key: fs.readFileSync("path/to/private/key.pem"), cert: fs.readFileSync("path/to/certificate.pem") }; http.createServer(app).listen(80); https.createServer(httpsOptions, app).listen(443) 6) Debugging Express
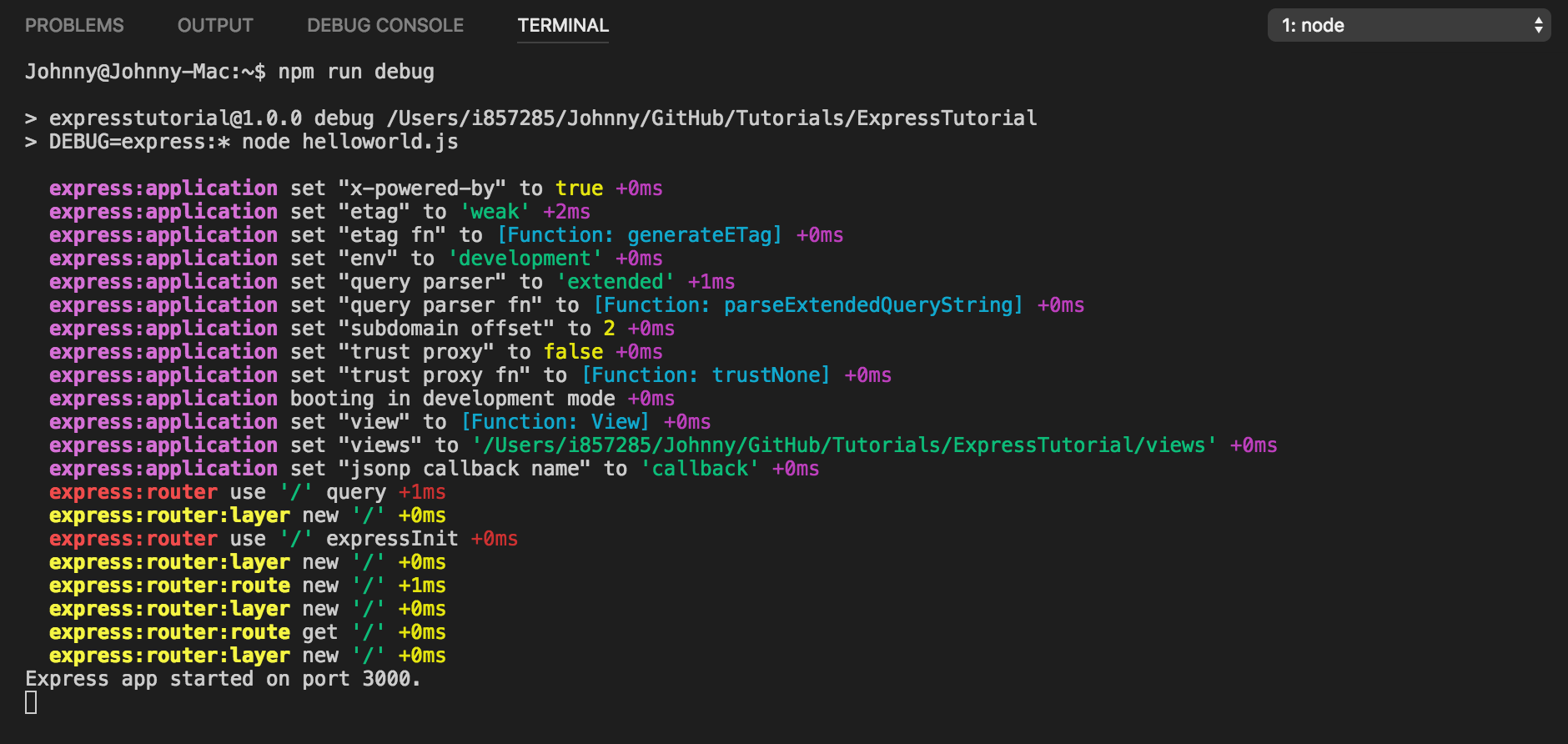
To see all the internal logs used in Express, set the DEBUG environment variable to express:* when launching your app.
"debug": "DEBUG=express:* node helloworld.js" Run ‘npm run debug’.