The @RepeatedTest annotation is used to write repeatable test templates that could run multiple times in JUnit. The repetition frequency can be configured as a parameter to @RepeatedTest annotation.
1. @RepeatedTest Annotation
The @RepeatedTest annotation is used to mark a test method that should repeat a specified number of times with a configurable display name.
To repeat a test with different arguments, consider using @ParameterizedTest.
1.1. Syntax
To create a repeatable test, annotate the test method with @RepeatedTest.
In the given example, the test method uses @RepeatedTest(5) annotation. It means that the test will be executed five times.
@DisplayName("Add operation test") @RepeatedTest(5) void addNumber(TestInfo testInfo) { Calculator calculator = new Calculator(); Assertions.assertEquals(2, calculator.add(1, 1), "1 + 1 should equal 2"); }1.2. Lifecycle Methods
Please note that each invocation of a repeated test behaves like the execution of a regular test with full support for the same lifecycle callbacks and extensions.
It means that @BeforeEach and @AfterEach annotated lifecycle methods will be invoked for each invocation of the test.
package com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples; import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll; import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions; import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll; import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach; import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName; import org.junit.jupiter.api.RepeatedTest; import org.junit.jupiter.api.RepetitionInfo; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.junit.jupiter.api.TestInfo; import org.junit.platform.runner.JUnitPlatform; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; @RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class) public class RepeatedTestExample { @BeforeAll public static void init(){ System.out.println("Before All init() method called"); } @BeforeEach public void initEach(){ System.out.println("Before Each initEach() method called"); } @DisplayName("Add operation test") @RepeatedTest(5) void addNumber(TestInfo testInfo, RepetitionInfo repetitionInfo) { System.out.println("Running addNumber test -> " + repetitionInfo.getCurrentRepetition()); Assertions.assertEquals(2, Calculator.add(1, 1), "1 + 1 should equal 2"); } @AfterEach public void cleanUpEach(){ System.out.println("After Each cleanUpEach() method called"); } @AfterAll public static void cleanUp(){ System.out.println("After All cleanUp() method called"); } }The output of the above test:
Before All init() method called Before Each initEach() method called After Each cleanUpEach() method called Before Each initEach() method called Running addNumber test -> 1 After Each cleanUpEach() method called Before Each initEach() method called Running addNumber test -> 2 After Each cleanUpEach() method called Before Each initEach() method called Running addNumber test -> 3 After Each cleanUpEach() method called Before Each initEach() method called Running addNumber test -> 4 After Each cleanUpEach() method called Before Each initEach() method called Running addNumber test -> 5 After Each cleanUpEach() method called After All cleanUp() method called 2. Custom Display Names
Apart from specifying the number of repetitions, we can give a custom display name to each repetition. This custom display name can be a combination of {static text + dynamic placeholders}.
Currently, three placeholders are supported:
{displayName}: display name of the@RepeatedTestmethod.{currentRepetition}: the current repetition count.{totalRepetitions}: the total number of repetitions.
public class JUnit5AnnotationsExample { @DisplayName("Add operation test") @RepeatedTest(value = 5, name = "{displayName} - repetition {currentRepetition} of {totalRepetitions}") void addNumber(TestInfo testInfo) { Assertions.assertEquals(2, Calculator.add(1, 1), "1 + 1 should equal 2"); } }Running the above test will output in below:
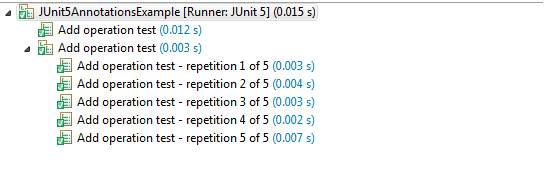
We can use one of two predefined formats i.e. LONG_DISPLAY_NAME and SHORT_DISPLAY_NAME. The latter is the default format if none is specified.
RepeatedTest.LONG_DISPLAY_NAME– {displayName} :: repetition {currentRepetition} of {totalRepetitions}RepeatedTest.SHORT_DISPLAY_NAME– repetition {currentRepetition} of {totalRepetitions}
@DisplayName("Add operation test") @RepeatedTest(value = 5, name = RepeatedTest.LONG_DISPLAY_NAME) void addNumber(TestInfo testInfo) { Assertions.assertEquals(2, Calculator .add(1, 1), "1 + 1 should equal 2"); }3. RepetitionInfo interface
RepetitionInfo is used to fetch information about the current repetition of a repeated test inside the @RepeatedTest, or lifecycle methods such as @BeforeEach, and @AfterEach.
public class JUnit5AnnotationsExample { @BeforeEach public void initEach(RepetitionInfo info){ int currentRepetition = info.getCurrentRepetition(); int totalRepetitions = info.getTotalRepetitions(); //Use information as needed } @DisplayName("Add operation test") @RepeatedTest(value = 5, name="{displayName} :: repetition {currentRepetition} of {totalRepetitions}") void addNumber(TestInfo testInfo) { Calculator calculator = new Calculator(); Assertions.assertEquals(2, calculator.add(1, 1), "1 + 1 should equal 2"); } @AfterEach public void cleanUpEach(RepetitionInfo info){ int currentRepetition = info.getCurrentRepetition(); int totalRepetitions = info.getTotalRepetitions(); //Use information as needed } }Happy Learning !!


Comments