Note: Sign in to access the data in this sample. username password
Getting Started
A knowledge graph allows you work with a graph network. This network connects people, places, and things (represented by entities) with each other through relationships that define how they are associated. Both entities and relationships can have associated properties. And an entity with a spatial location can be connected with other entities that do not have a spatial location.
This sample demonstrates searching a knowledge graph executeSearchStreaming().
The sample dataset contains observations of bumble bees made at locations around the United States. Each observation was made and verified by users and is of a specific species of bumble bee.
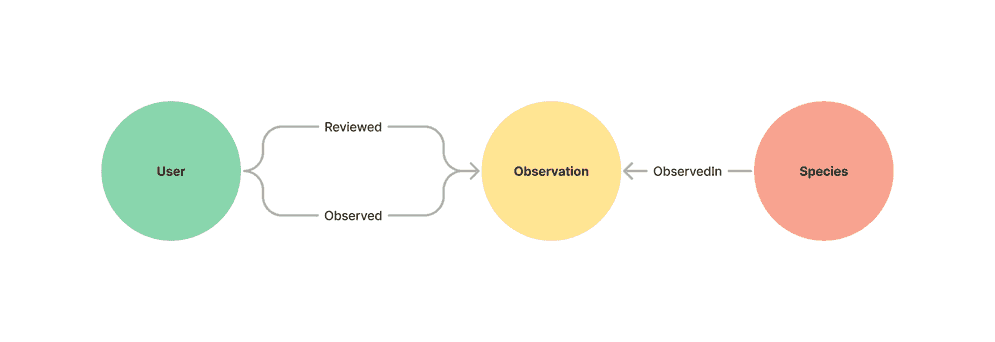
Good search terms include states abbreviations (e.g. CA, WA), countries, parks, and bumble bee descriptors (e.g. fuzzy, yellow, spotted).
For additional information on working with knowledge graph services see:
- Introduction to Knowledge Graph in the JavaScript Maps SDK.
- Working with knowledge graph layers
- Query a knowledge graph
- Edit knowledge graph data
- Get started with ArcGIS Knowledge Server for overview of ArcGIS Knowledge for ArcGIS Enterprise.
- Hosted Knowledge Graph Service for information on managing knowledge graph services via ArcGIS Enterprise and the REST API.
- Get started with ArcGIS Knowledge (ArcGIS Pro) for information on ArcGIS Knowledge in ArcGIS Pro.
How to use this sample
1. Sign in
The data in this example is secured, as most knowledge graph data will be since the ArcGIS Knowledge Graph Server license is required. Therefore, the first step is to sign in to load the data.
In this sample sign in with the following credentials: username password.
2. Enter search term
Enter a search term. The default search term is "bombus" (Latin name for the genus bumble bee) but you can provide any search term such as "yellow" for yellow-tailed bumble bee or "california" for all observations made in the state.

3. Specify Parameters
Specify whether to search for the term just in the properties of entities, just in the properties of relationships, or in the properties of both.

To search with no additional parameters, run the search.
Optional properties
Streaming search has the following optional properties.
-
Start index
The record index to start the search. All records before this index will be ignored.
-
Maximum number of records
The maximum number of records to return from the search. By default this is not specified so all results will be returned unless the number of results exceeds the
maxparameter in theRecord Count serviceof the knowledge graph. If theDefinition maxis reached, then it will return all results up to that limit.Record Count -
Named types to search
Limit the search to specific entity or relationship types. Any number of types can be specified. All types are searched by default.
-
IDs to search
Limit the search to specific record ids. Any number of ids can be specified. All ids are searched by default.
-
Return search context
If checked, the result also returns the names of the properties that matched the search term for each record, and the scores of how well each result matches the search term.
4. Run the search
The search may take a few seconds to return results. The records with properties that match the search term are listed, with the first one selected to show it's properties. Select any returned result to see it's properties.
How it Works
The first step is to connect to a knowledge graph using fetchKnowledgeGraph. This returns the service definition and data model for the knowledge graph. You can then use the data model to populate the list of entity types and relationship types that are in the graph.
// set knowledge graph with url to service const url = "https://sampleserver7.arcgisonline.com/server/rest/services/Hosted/BumbleBees/KnowledgeGraphServer"; const knowledgeGraph = await knowledgeGraphService.fetchKnowledgeGraph(url); const typeSelect = document.getElementById("streaming-search-named-types"); const searchButton = document.getElementById('streaming-search-button'); //use the knowledge graph data model to create the dropdowns for the named type selection knowledgeGraph.dataModel.entityTypes.forEach((entityType) => { typeSelect.innerHTML += `<calcite-combobox-item value="${entityType.name}" heading="${entityType.name}"></calcite-combobox-item>`; }) knowledgeGraph.dataModel.relationshipTypes.forEach((relType) => { typeSelect.innerHTML += `<calcite-combobox-item value="${relType.name}" heading="${relType.name}"></calcite-combobox-item>`; }) Streaming search returns results in small chunks allowing the client to begin processing the data returned immediately rather than waiting for the entire result set to be returned before processing. Streaming is faster, more efficient, and will retrieve all matching records, even if the total exceeds the search limits set in the service definition. Another benefit of streaming is that the request is encoded which means that it is far smaller than a traditional HTTP GET or JSON POST body.
//Search the graph using the options provided. //only the search term and typeCategoryFilter are required as search parameters searchButton.addEventListener('click', async (e) => { //get search inputs const searchString = document.getElementById("streaming-search-keyword").value const typeFilter = document.getElementById("streaming-search-type-filter").value const namedTypes = document.getElementById("streaming-search-named-types").value const index = document.getElementById("streaming-search-start-index").value const limit = document.getElementById("streaming-search-limit").value const ids = document.getElementById("streaming-search-ids").value const context = document.getElementById('streaming-search-context').checked //construct the search object const searchParams = { searchQuery: searchString, typeCategoryFilter: typeFilter, returnSearchContext: context, } if (index) { searchParams["start"] = index }; if (limit) { searchParams["num"] = limit }; if (namedTypes) { searchParams["namedTypesFilter"] = typeof namedTypes == "string" ? [namedTypes] : namedTypes }; if (ids) { searchParams["idsFilter"] = [ids] }; //execute the search and read the result const searchResults = await knowledgeGraphService.executeSearchStreaming(knowledgeGraph, searchParams) readStream(searchResults); }) Each chunk returned by a streaming search is a readable stream that must be read before the results can be used. After the chunk is read it can be used in other client side processing. In this case it is used to create and display of the result.
// a function to read the stream returned from the streaming search const readStream = async (streamingQueryResult) => { //create the reader let reader = streamingQueryResult.resultRowsStream.getReader(); //try to read the stream try { while (true) { //read the stream const { done, value } = await reader.read(); if (done) { break; } createList(value) } // if there is an error in returning the stream or the stream is aborted } catch (err) { if (err.name === "AbortError") { console.log("Request aborted as expected"); } else { throw err; } } };