| I am a Research Scientist at Meta Reality Labs Research. I did my Ph.D. with Prof. Matthias Nießner at Visual Computing Group, at the Technical University of Munich. I received a Master's Degree in Computer Science from the Technical University of Munich and a Bachelor's Degree in Mathematics from the University of Ljubljana. I'm interested in computer vision, graphics and AI. My research is mostly focused on neural rendering and generative AI, especially when it comes to modelling 3D deformable objects, with applications in VR/AR, robotics, etc. Email | Google Scholar | Twitter | Github |  |
| |
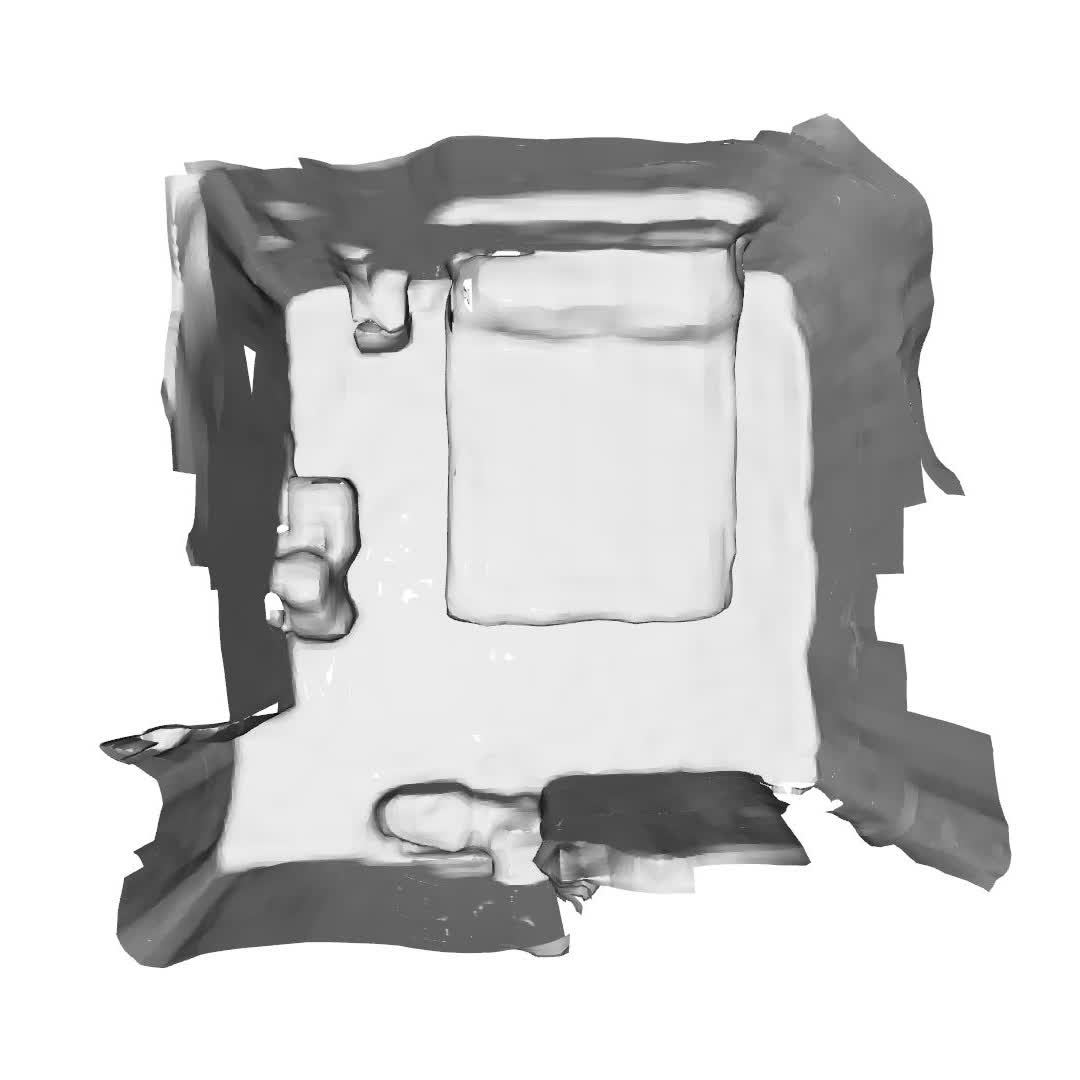
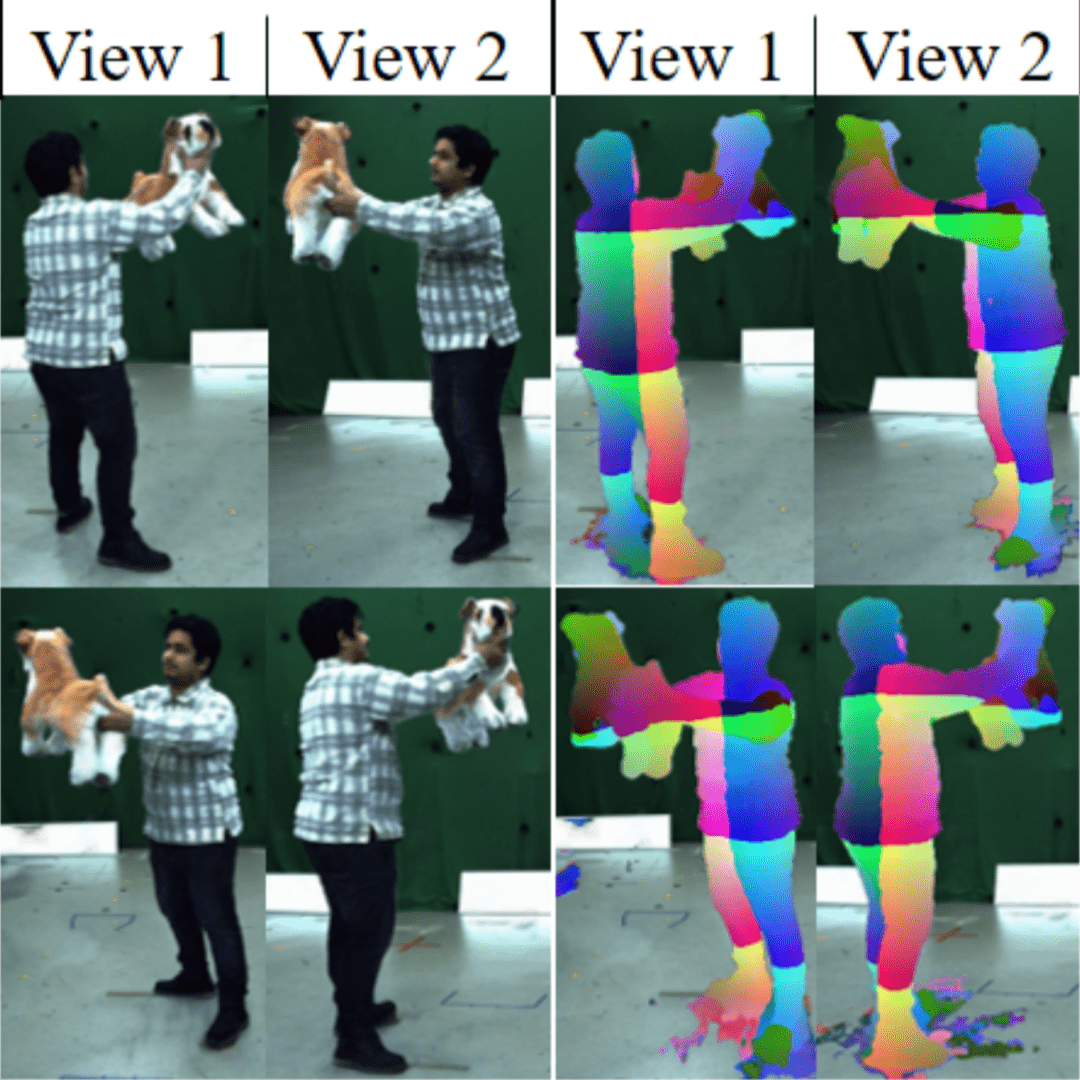
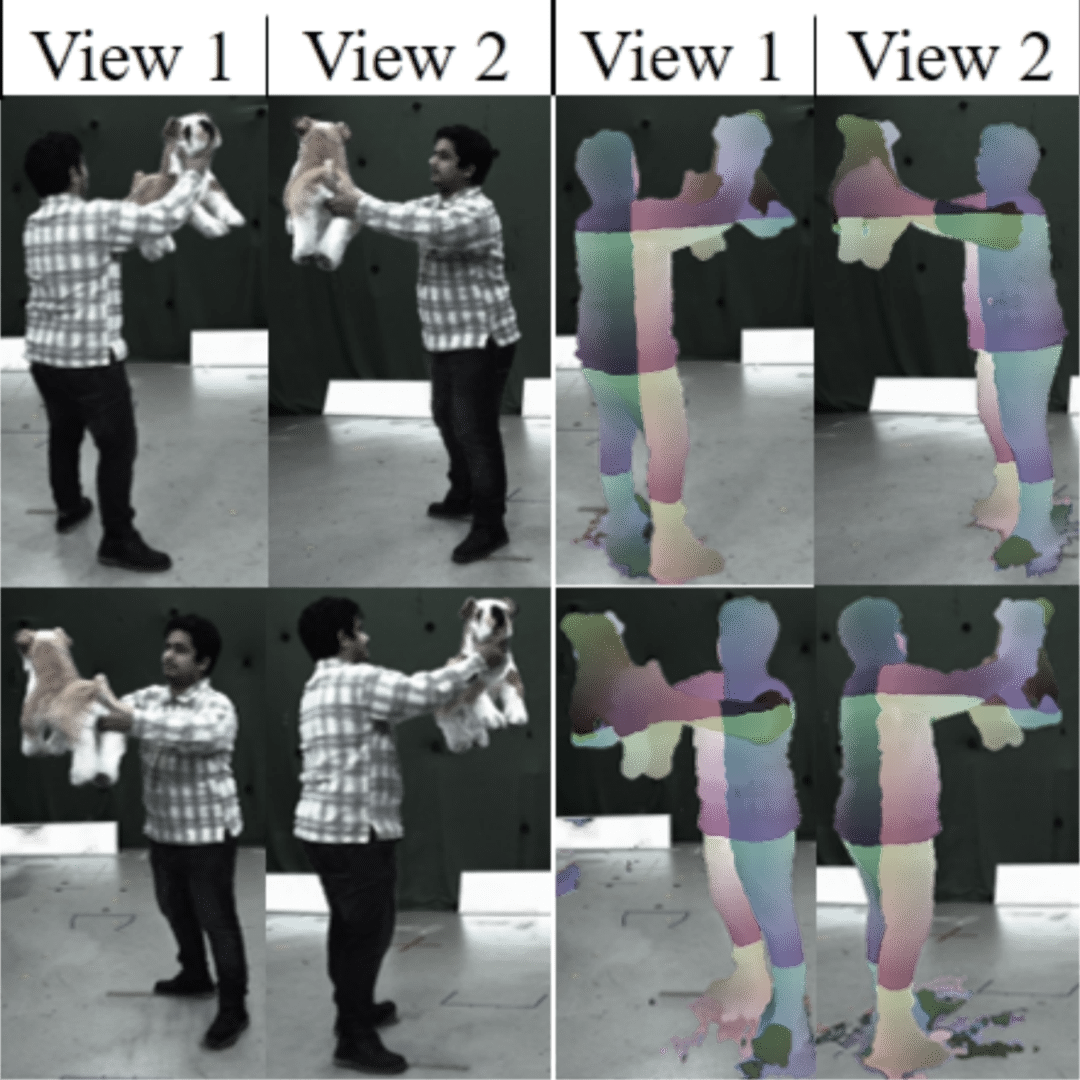
| Edith Tretschk, Vladislav Golyanik, Michael Zollhöfer, Aljaž Božič, Christoph Lassner, Christian Theobalt 3DV 2024 paper | video | bibtex We propose SceNeRFlow to reconstruct a general, non-rigid scene in a time-consistent manner. Our dynamic-NeRF method takes multi-view RGB videos and background images from static cameras with known camera parameters as input. We use a backwards deformation model and can accurately model long studio-scale motions. | |
| Ziyan Wang, Giljoo Nam, Aljaž Božič, Chen Cao, Jason Saragih, Michael Zollhöfer, Jessica Hodgins 3DV 2024 paper | bibtex We present a novel local appearance model that is capable of capturing the photorealistic appearance of diverse hairstyles in a volumetric way. Our method leverages the local similarity across different hairstyles and learns a universal hair appearance prior from multi-view captures of hundreds of people. | |
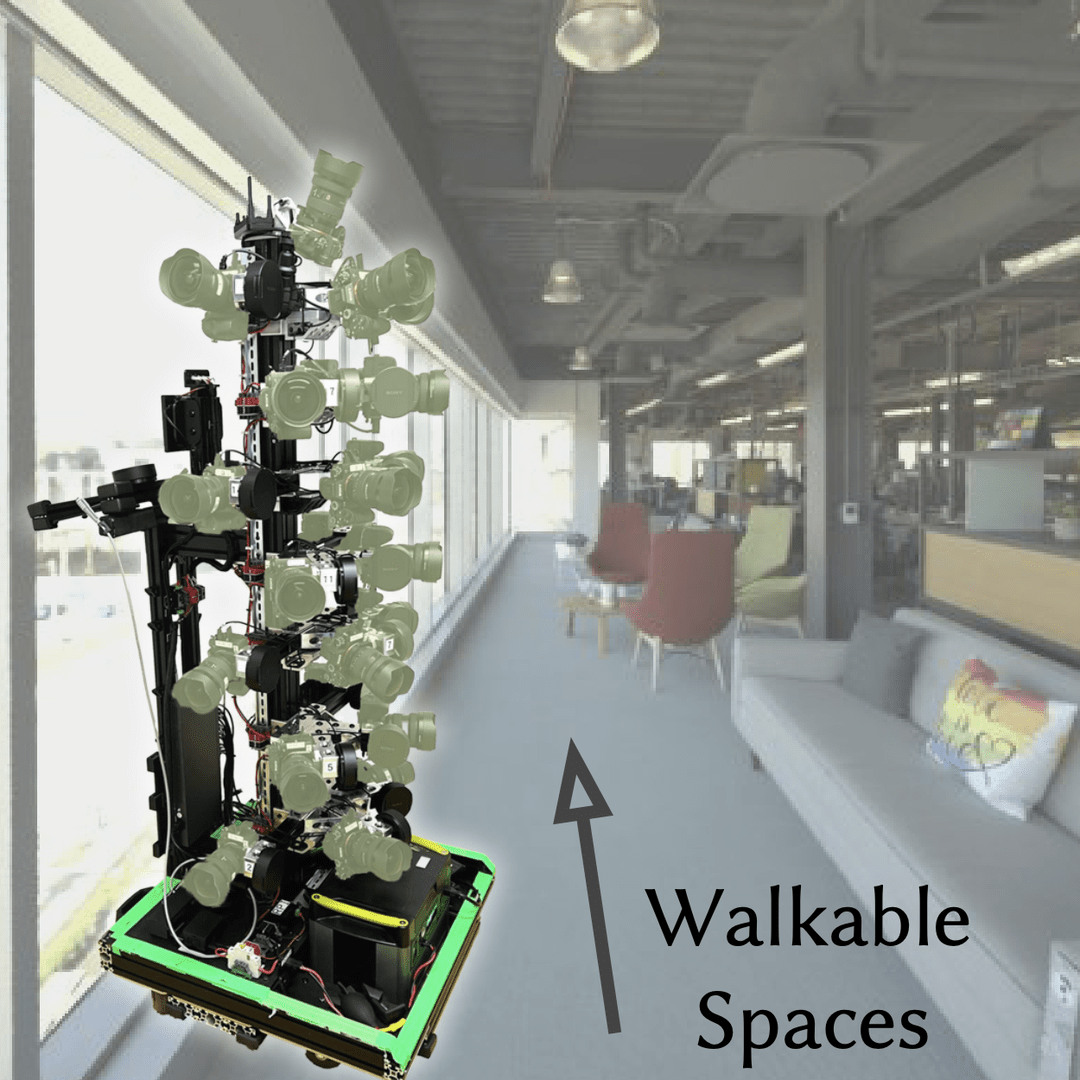
| Linning Xu, Vasu Agrawal, William Laney, Tony Garcia, Aayush Bansal, Changil Kim, Samuel Rota Bulò, Lorenzo Porzi, Peter Kontschieder, Aljaž Božič, Dahua Lin, Michael Zollhöfer, Christian Richardt SIGGRAPH Asia 2023 paper | video | bibtex VR-NeRF brings high-fidelity walkable spaces to real-time virtual reality. Our “Eyeful Tower” multi-camera rig captures spaces with high image resolution and dynamic range that approach the limits of the human visual system. | |
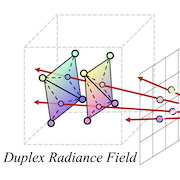
| Ziyu Wan, Christian Richardt, Aljaž Božič, Chao Li, Vijay Rengarajan, Seonghyeon Nam, Xiaoyu Xiang, Tuotuo Li, Bo Zhu, Rakesh Ranjan, Jing Liao CVPR 2023 paper | video | bibtex We introduce a novel approach to distill and bake NeRFs into highly efficient mesh-based neural representations that are fully compatible with the massively parallel graphics rendering pipeline. We represent scenes as neural radiance features encoded on a two-layer duplex mesh, which effectively overcomes the inherent inaccuracies in 3D surface reconstruction. | |
| Wenqi Xian, Aljaž Božič, Noah Snavely, Christoph Lassner CVPR 2023 paper | bibtex We propose NeuroLens, a neural lens model for distortion and vignetting that can be used for point projection and ray casting and can be optimized through both operations. This means that it can (optionally) be used to perform pre-capture calibration using classical calibration targets, and can later be used to perform calibration or refinement during 3D reconstruction, e.g., while optimizing a radiance field. | |
| Aljaž Božič, Denis Gladkov, Luke Doukakis, Christoph Lassner arXiv 2022 paper | video | bibtex We propose a novel neural representation for capturing real-world objects in everyday environments, featuring photorealistic appearance and volumetric effects, such as translucent object parts. Our real-time model architecture is transpiled into efficient shader code seamlessly integrated into a modern game engine, supporting object interactions, shadows, etc. | |
| Di Chang, Aljaž Božič, T. Zhang, Q. Yan, Y. Chen, S. Süsstrunk, Matthias Nießner ECCV 2022 paper | code | video | bibtex We introduce RC-MVSNet, an unsupervised multi-view stereo reconstruction approach that leverages NeRF-like rendering to generate consistent photometric supervision for non-Lambertian surfaces, and propose an improved Gaussian-Uniform sampling to overcome occlusion artifacts present in existing approaches. | |
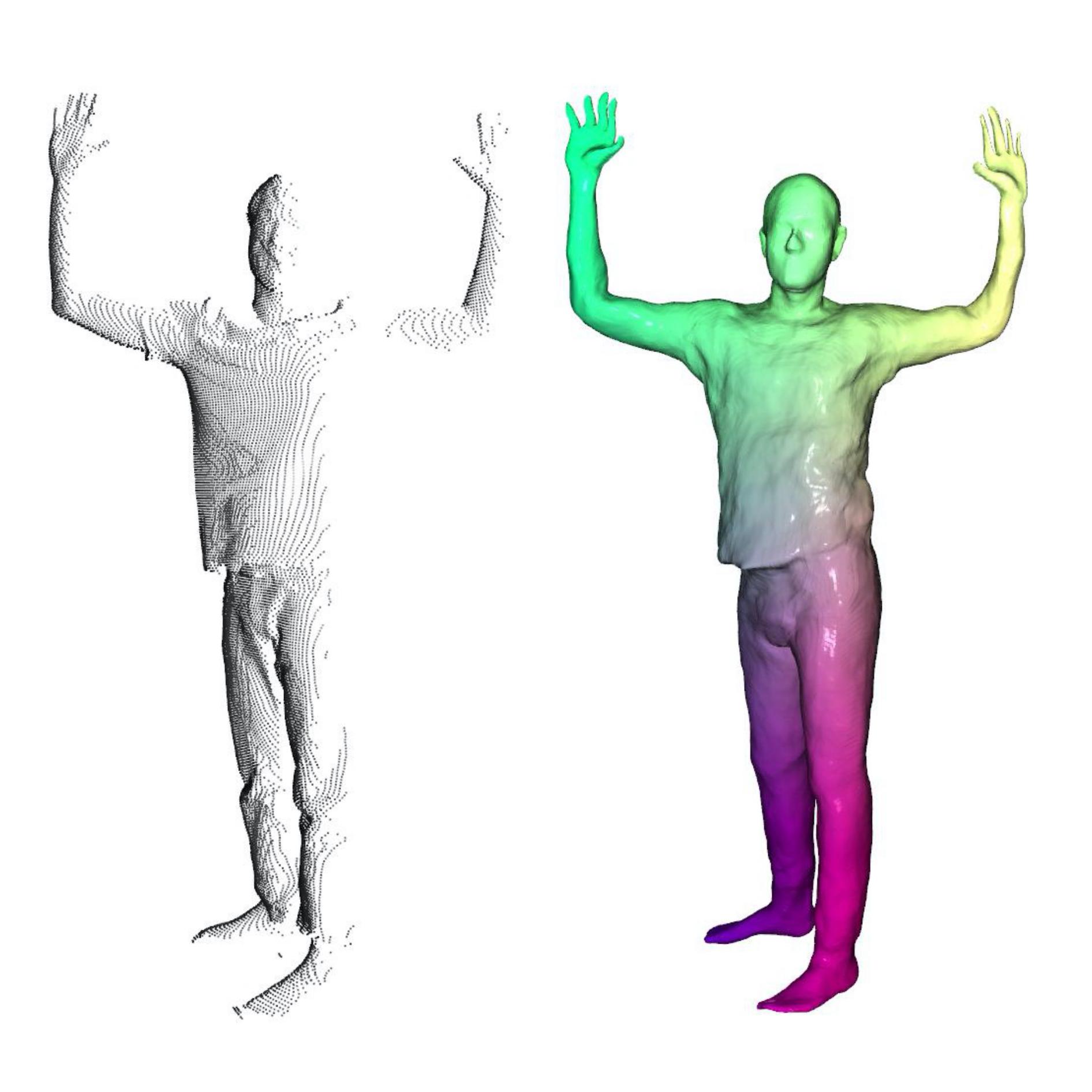
| Aljaž Božič, Pablo Palafox, Justus Thies, Angela Dai, Matthias Nießner NeurIPS 2021 paper | code | video | bibtex We introduce TransformerFusion, a transformer-based 3D scene reconstruction approach. The input monocular RGB video frames are fused into a volumetric feature representation of the scene by a transformer network that learns to attend to the most relevant image observations, resulting in an accurate online surface reconstruction. | |
| Pablo Palafox, Aljaž Božič, Justus Thies, Matthias Nießner, Angela Dai ICCV 2021 paper | code | video | bibtex We propose Neural Parametric Models (NPMs), a learned alternative to traditional, parametric 3D models. 4D dynamics are disentangled into latent-space representations of shape and pose, leveraging the flexibility of recent developments in learned implicit functions. Once learned, NPMs enable optimization over the learned spaces to fit to new observations. | |
| Aljaž Božič, Pablo Palafox, Michael Zollhöfer, Justus Thies, Angela Dai, Matthias Nießner CVPR 2021 (Oral) paper | code | video | bibtex We introduce Neural Deformation Graphs for globally-consistent deformation tracking and 3D reconstruction of non-rigid objects. Specifically, we implicitly model a deformation graph via a deep neural network and empose per-frame viewpoint consistency as well as inter-frame graph and surface consistency constraints in a self-supervised fashion. | |
| Aljaž Božič*, Pablo Palafox*, Michael Zollhöfer, Angela Dai, Justus Thies, Matthias Nießner NeurIPS 2020 paper | code | video | bibtex We introduce a novel, end-to-end learnable, differentiable non-rigid tracker that enables state-of-the-art non-rigid reconstruction. By enabling gradient back-propagation through a non-rigid as-rigid-as-possible optimization solver, we are able to learn correspondences in an end-to-end manner such that they are optimal for the task of non-rigid tracking. | |
| Yang Li, Aljaž Božič, Tianwei Zhang, Yanli Ji, Tatsuya Harada, Matthias Nießner CVPR 2020 (Oral) paper | video | bibtex We learn the tracking of non-rigid objects by differentiating through the underlying non-rigid solver. Specifically, we propose ConditionNet which learns to generate a problem-specific preconditioner using a large number of training samples from the Gauss-Newton update equation. The learned preconditioner increases PCG’s convergence speed by a significant margin. | |
| Aljaž Božič, Michael Zollhöfer, Christian Theobalt, Matthias Nießner CVPR 2020 paper | dataset | video | bibtex We present a large dataset of 400 scenes, over 390,000 RGB-D frames, and 5,533 densely aligned frame pairs, and introduce a data-driven non-rigid RGB-D reconstruction approach using learned heatmap correspondences, achieving state-of-the-art reconstruction results on a newly established quantitative benchmark. | |
| Aljaž Božič*, Nikolas Brasch*, Joe Lallemand, Federico Tombari IROS 2018 paper | bibtex We propose a semantic monocular SLAM framework designed to deal with highly dynamic environments, combining feature-based and direct approaches to achieve robustness under challenging conditions. Our approach uses deep-learned semantic information extracted from the scene to cope with outliers on dynamic objects. | |
| Georg Kuschk, Aljaž Božič, Daniel Cremers IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2017 paper | bibtex We propose an algorithm for dense and direct large-scale visual SLAM that runs in real-time on a commodity notebook. A fast variational dense 3D reconstruction algorithm was developed which robustly integrates data terms from multiple images. Embedded into a keyframe-based SLAM framework it enables us to densely reconstruct large scenes. |
| |
| Source code stolen from Jon Barron. |